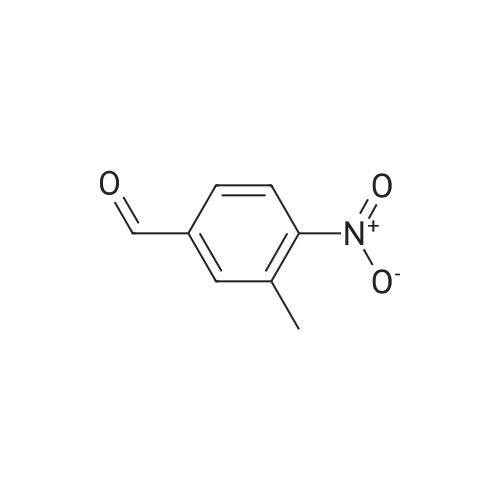
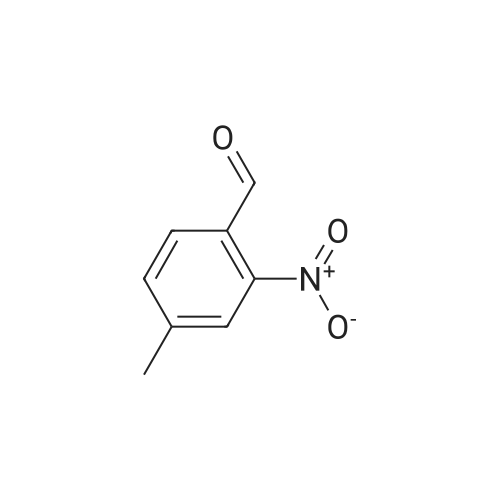
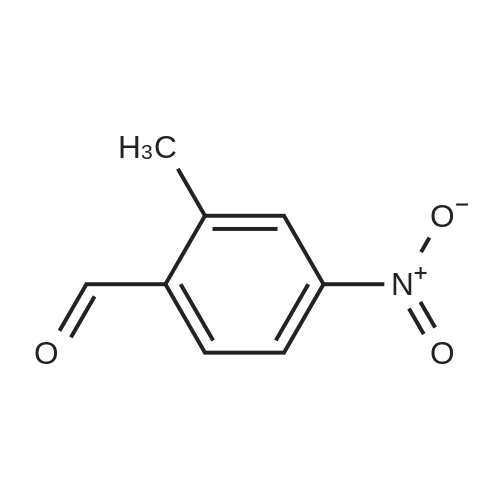
Design and synthesis of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-chalcone conjugates as antikinetoplastid agents
Agarwal, Devesh S.
;
Beteck, Richard M.
;
Ilbeigi, Kayhan
, et al.
Chem. Biol. Drug Des.,2024,103(1):e14400.
DOI:
10.1111/cbdd.14400
PubMed ID:
37994272
More
Abstract: A library of imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-appended chalcones were synthesized and characterized using 1H NMR,13C NMR and HRMS. The synthesized analogs were screened for their antikinetoplastid activity against Trypanosoma cruzi, Trypanosoma brucei brucei, Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense and Leishmania infantum. The analogs were also tested for their cytotoxicity activity against human lung fibroblasts and primary mouse macrophages. Among all screened derivatives, (E)-N-(4-(3-(2-chlorophenyl)acryloyl)phenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxamide was found to be the most active against T. cruzi and T. b. brucei exhibiting IC50 values of 8.5 and 1.35 μM, resp. Against T. b. rhodesiense, (E)-N-(4-(3-(4-bromophenyl)acryloyl)phenyl)imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine-2-carboxamide was found to be the most active with an IC50 value of 1.13 μM. All synthesized active analogs were found to be non-cytotoxic against MRC-5 and PMM with selectivity indexes of up to more than 50.
Keywords:
antikinetoplastid ;
chalcone ;
drug likeliness properties ;
imidazo[1,2-a]pyridine ;
neglected tropical diseases (NTDs) ;
Trypanosoma brucei brucei ;
Trypanosoma brucei rhodesiense
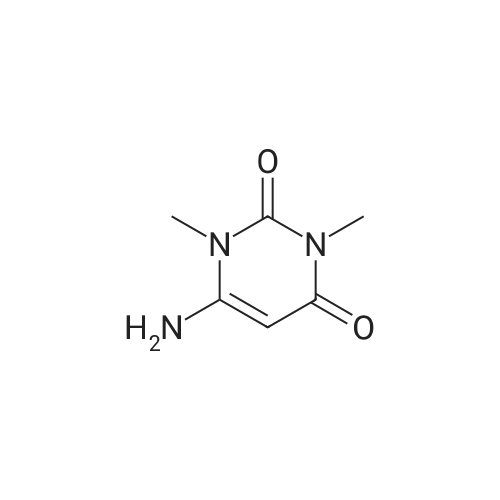
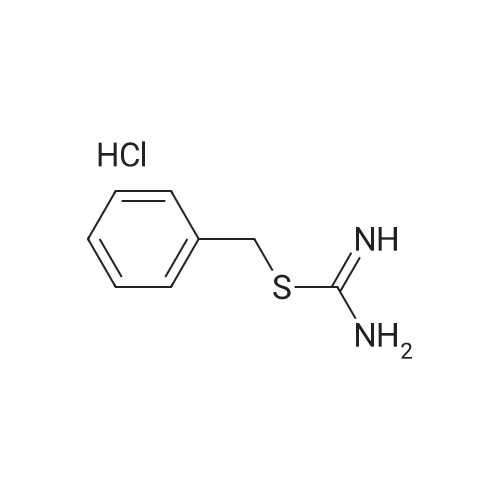
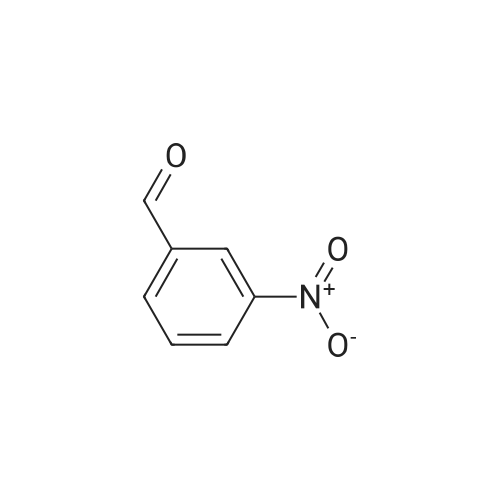
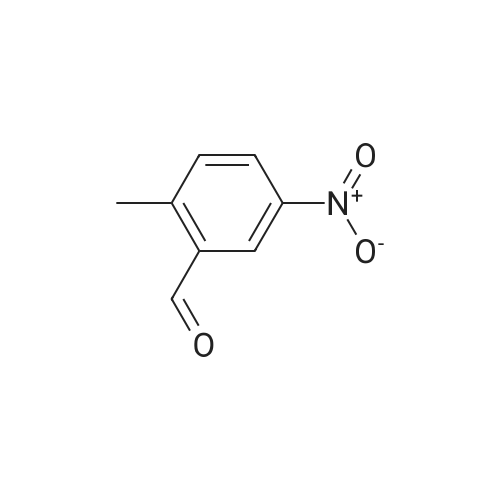
Purchased from AmBeed:
613-45-6 ;
587-04-2 ;
1122-91-4 ;
64951-08-2 ;
99-92-3 ;
99-92-3 ;
456-48-4 ;
555-16-8 ;
94-41-7 ;
104-88-1 ;
1113-59-3 ;
459-57-4 ;
529-20-4 ;
6287-38-3 ;
1113-59-3

Are β-Lactones Involved in Carbon-Based Olefination Reactions?
Jan Nowak
;
Micha? Tryniszewski
;
Micha? Barbasiewicz
Synlett,2024,35(10):1190-1194.
DOI:
10.1055/a-2268-4386
More
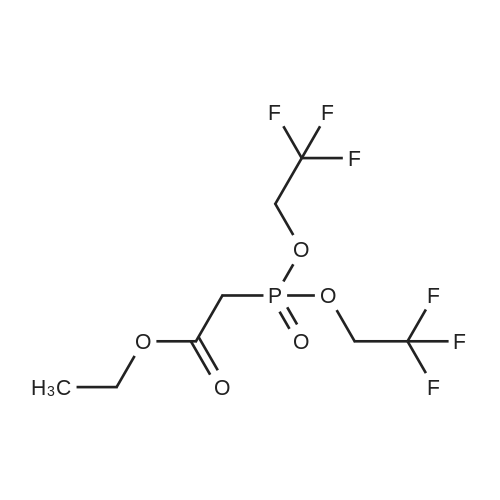
Abstract: Heteroatom-based olefinating reagents (e.g., organic phosphonates, sulfonates, etc.) are used to transform carbonyl compounds into alkenes, and their mechanism of action involves aldol-type addition, cyclization, and fragmentation of four-membered ring intermediates. We have developed an analogous process using ethyl 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexafluoroisopropyl methylmalonate, which converts electrophilic aryl aldehydes into α-methylcinnamates in up to 70% yield. The reaction plausibly proceeds through the formation of β-lactone that spontaneously decarboxylates under the reaction conditions. The results shed light on the Knoevenagel–Doebner olefination, for which decarboxylative anti-fragmentation of aldol-type adducts is usually considered.
Keywords:
olefination ;
carbonyl compounds ;
reaction mechanism ;
lactones ;
malonates ;
Knoevenagel ;
Doebner reaction
Purchased from AmBeed:
587-04-2 ;
609-08-5 ;
29166-72-1 ;
99-61-6 ;
555-16-8 ;
104-88-1 ;
6674-22-2
Metal-Free, Rapid, and Highly Chemoselective Reduction of Aromatic Nitro Compounds at Room Temperature
Jang, Mingyeong
;
Lim, Taeho
;
Park, Byoung Yong
, et al.
JOC,2022,87(2):910-919.
DOI:
10.1021/acs.joc.1c01431
PubMed ID:
34983185
More
Abstract: In this study, we developed a metal-free and highly chemoselective method for the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds. This reduction was performed using tetrahydroxydiboron [B2(OH)4] as the reductant and 4,4'-bipyridine as the organocatalyst and could be completed within 5 min at room temperature. Under optimal conditions, nitroarenes with sensitive functional groups, such as vinyl, ethynyl, carbonyl, and halogen, were converted into the corresponding anilines with excellent selectivity while avoiding the undesirable reduction of the sensitive functional groups.
Purchased from AmBeed:
607-35-2 ;
578-66-5 ;
613-50-3 ;
100-19-6 ;
579-71-5 ;
3034-94-4 ;
5683-43-2 ;
99-92-3 ;
13534-97-9 ;
5676-60-8 ;
5470-18-8 ;
619-45-4 ;
553-26-4 ;
580-15-4 ;
611-34-7 ;
619-72-7 ;
100-13-0 ;
540-37-4 ;
1849-25-8 ;
4487-59-6 ;
555-16-8 ;
6298-19-7 ;
556-08-1 ;
953-26-4 ;
54060-30-9 ;
62-23-7 ;
607-34-1 ;
3867-18-3 ;
873-74-5 ;
3544-24-9 ;
94-52-0 ;
1520-21-4 ;
5470-34-8 ;
619-50-1 ;
586-39-0 ;
934-22-5 ;
402-54-0 ;
15411-43-5 ;
455-14-1 ;
17763-80-3 ;
3085-54-9 ;
1942-30-9 ;
1694-20-8 ;
6305-66-4 ;
41656-75-1 ;
6393-17-5 ;
4309-66-4
...More



 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping