| 77% |
With sulfuric acid; iodine; periodic acid; In water; acetic acid; at 60℃; for 4.5h; |
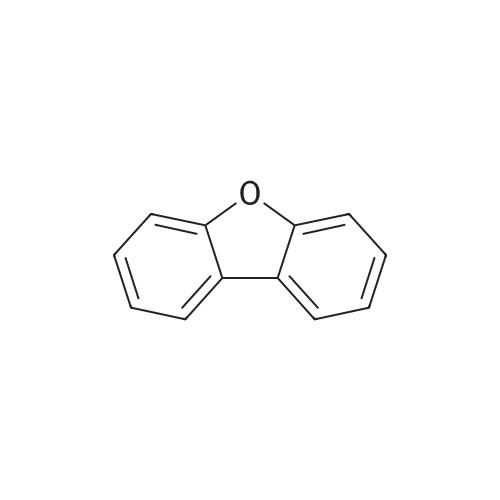
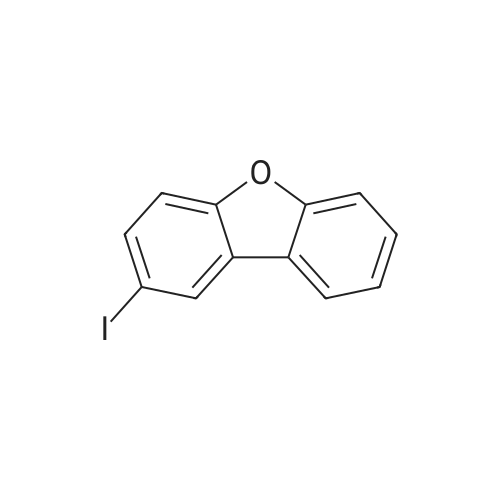
[Step 1: Method of Synthesizing 2-Iododibenzofuran]In a 500-mL three-neck flask was put a suspension of 8.4 g (50 mmol) of dibenzofuran, 6.2 g (25 mmol) of iodine, 5.7 g (25 mmol) of orthoperiodic acid, 150 mL of glacial acetic acid, 30 mL of water, and 500 muL of sulfuric acid, and the suspension was heated and stirred at 60 C. for 4.5 hours to cause a reaction.After the reaction, the reaction mixture was further stirred at room temperature for 16 hours. The generated precipitate was collected by filtration, and the resulting matter was dissolved in 150 mL of toluene. Then, the solution was washed with water three times. Magnesium sulfate was added to the toluene solution to adsorb moisture.This solution was filtered, and the resulting filtrate was concentrated. Then, hexane was added thereto, followed by irradiation with ultrasonic waves. The generated solid was collected by filtration and dried, so that the objective substance was obtained as 11.3 g of white powder in 77% yield. A reaction scheme of this synthesis method is shown in (B-1) below. The compound obtained in Step 1 was subjected to a nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) measurement. The measurement data are shown below.1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz):delta (ppm)=7.33-7.38 (m, 2H), 7.48 (dt, J=1.5 Hz, 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (dd, J=2.1 Hz, 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (d, J=1.5 Hz, 1H).The measurement results confirmed that the objective substance, 2-iododibenzofuran, was obtained. |
| 77% |
With iodine; periodic acid;sulfuric acid; In water; acetic acid; at 60℃; for 4.5h; |
Step 1: Method of Synthesizing 2-Iododibenzofuran In a 500 mL three-neck flask was put a suspension of 8.4 g (50 mmol) of dibenzofuran, 6.2 g (25 mmol) of iodine, 5.7 g (25 mmol) of orthoperiodic acid, 150 mL of glacial acetic acid, 30 mL of water, and 500 muL of sulfuric acid, and the suspension was heated and stirred at 60 C. for 4.5 hours to cause a reaction. After the reaction, the reaction mixture was further stirred at room temperature for 16 hours. The generated precipitate was collected by filtration, and this obtained residue was dissolved in 150 mL of toluene. Then, the solution was washed with water three times. Magnesium sulfate was added to the toluene solution to adsorb moisture. This solution was filtered, and the obtained filtrate was concentrated. Then, hexane was added thereto, and the mixture was irradiated with ultrasonic waves. The generated solid was collected by filtration and dried to give 11.3 g of a white powder in 77% yield, which was the object of the synthesis. A reaction scheme of the above synthesis method is illustrated in (B-1) below. The compound obtained in Step 1 above was subjected to nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The measurement data are shown below. 1H NMR (CDCl3, 300 MHz): delta (ppm)=7.33-7.38 (m, 2H), 7.48 (dt, J=1.5 Hz, 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.56 (d, J=8.1 Hz, 1H), 7.72 (dd, J=2.1 Hz, 8.4 Hz, 1H), 7.95 (d, J=7.8 Hz, 1H), 8.27 (d, J=1.5 Hz, 1H). |
| 30.4% |
With [bis(acetoxy)iodo]benzene; sulfuric acid; iodine; acetic anhydride; acetic acid; for 2h; |
Exemplified Compound 1-1, 30 g (0.178 mol)340 ml of acetic acid, 60 ml of acetic anhydride and 26.1 g (× 0.455 mol) of iodobenzene diacetate were mixed and dissolved by stirring. To this solution, 20.6 g (× 0.455 mol) of iodine and 0.5 ml of sulfuric acid were alternately added in 10 minutes. And the mixture was further stirred for 2 hours.Precipitated crystals were filtered under reduced pressure. 100 ml of ethanol was added to the obtained crystals, and the suspension was refluxed for 30 minutes. After stirring at room temperature for 1 hour, filtration under reduced pressure gave exemplified compound 3-1, 15.9 g. (Yield 30.4%) |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping