Extensive Thiol Profiling for Assessment of Intracellular Redox Status in Cultured Cells by HPLC-MS/MS
Wu, Jiandong
;
Chernatynskaya, Anna
;
Pfaff, Annalise
, et al.
Antioxidants,2022,11(1):24.
DOI:
10.3390/antiox11010024
PubMed ID:
35052528
More
Abstract: Oxidative stress may contribute to the pathol. of many diseases, and endogenous thiols, especially glutathione (GSH) and its metabolites, play essential roles in the maintenance of normal redox status. Understanding how these metabolites change in response to oxidative insult can provide key insights into potential methods of prevention and treatment. Most existing methodologies focus only on the GSH/GSH disulfide (GSSG) redox couple, but GSH regulation is highly complex and depends on several pathways with multiple redox-active sulfur-containing species. In order to more fully characterize thiol redox status in response to oxidative insult, a high-performance liquid chromatog. with tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method was developed to simultaneously determine seven sulfur-containing metabolites, generating a panel that systematically examines several pathways involved in thiol metabolism and oxidative stress responses. The sensitivity (LOQ as low as 0.01 ng/mL), accuracy (88-126% spike recovery), and precision (=12% RSD) were comparable or superior to those of existing methods. Addnl., the method was used to compare the baseline thiol profiles and oxidative stress responses of cell lines derived from different tissues. The results revealed a previously unreported response to oxidative stress in lens epithelial (B3) cells, which may be exploited as a new therapeutic target for oxidative-stress-related ocular diseases. Further application of this method may uncover new pathways involved in oxidative-stress-related diseases and endogenous defense mechanisms.
Keywords:
HPLC-MS/MS ;
biomarker ;
cancer cells ;
glutathione ;
lens epithelial cells ;
thiol
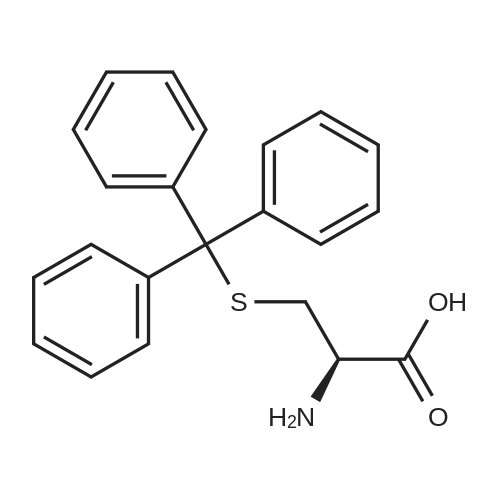
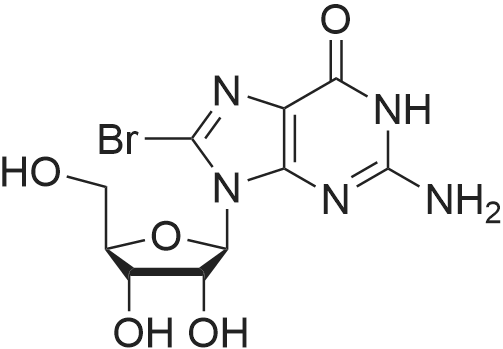
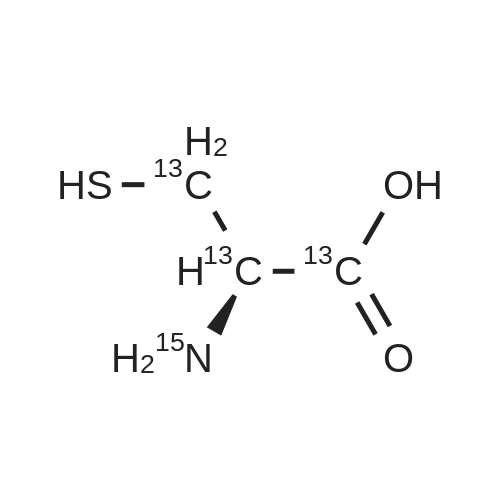
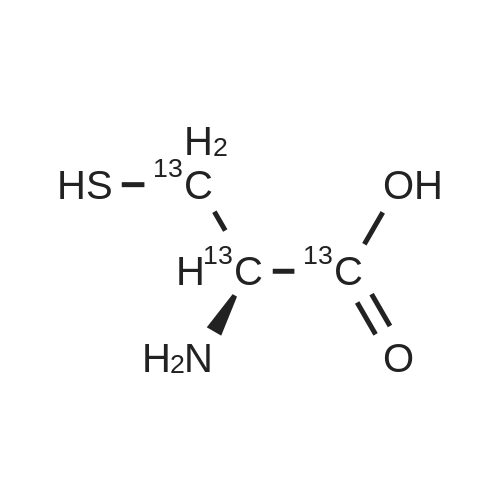
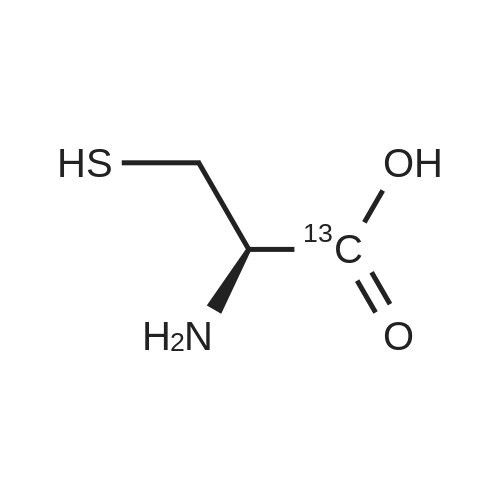
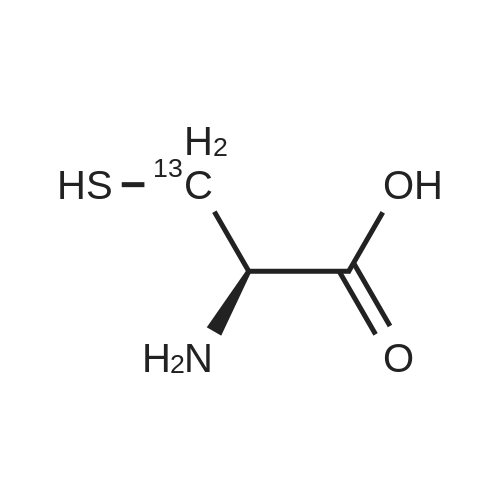
Purchased from AmBeed:
52-90-4

Development of a HPLC-MS/MS method for assessment of thiol redox status in human tear fluids
Wu, Jiandong
;
Sigler, Austin
;
Pfaff, Annalise
, et al.
Anal. Biochem.,2021,629,114295.
DOI:
10.1016/j.ab.2021.114295
PubMed ID:
34186074
More
Abstract: Oxidative stress is reported to be part of the pathol. of many ocular diseases. For the diagnosis of ocular diseases, tear fluid has unique advantages. Although numerous anal. methods exist for the measurement of different types of biomols. in tear fluid, few have been reported for comprehensive understanding of oxidative stress-related thiol redox signaling. In this study, a high-performance liquid chromatog.-tandem mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) method was developed to determine a panel of twelve metabolites that systematically covered several thiol metabolic pathways. With optimization of MS/MS parameters and HPLC mobile phases, this method was sensitive (LOQ as low as 0.01 ng/mL), accurate (80-125% spike recovery) and precise (<10% RSD). This LC-MS/MS method combined with a simple tear fluid collection with Schirmer test strip followed by ultrafiltration allowed the high-throughput anal. for efficient determination of metabolites associated with thiol redox signaling in human tear fluids. The method was then applied to a small cohort of tear fluids obtained from healthy individuals. The method presented here provides a new technique to facilitate future work aiming to determine the complex thiol redox signaling in tear fluids for accurate assessment and diagnosis of ocular diseases.
Keywords:
Biomarker ;
Glutathione ;
HPLC-MS/MS ;
Ocular disease ;
Tear fluid ;
Thiol
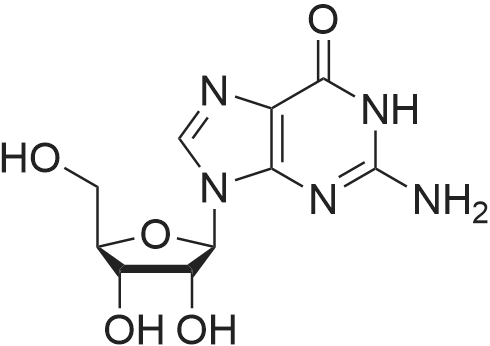
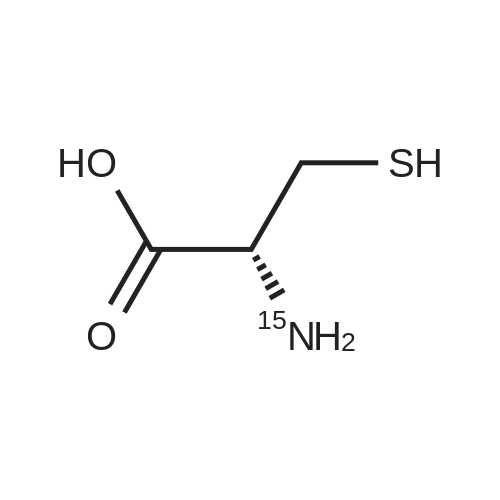
Purchased from AmBeed:
52-90-4 ;
923-32-0


 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping