| 1% |
With lithium diisopropyl amide; In tetrahydrofuran; tetrahydrofuran-heptane-ethylbenzene; ethanol; dichloromethane; |
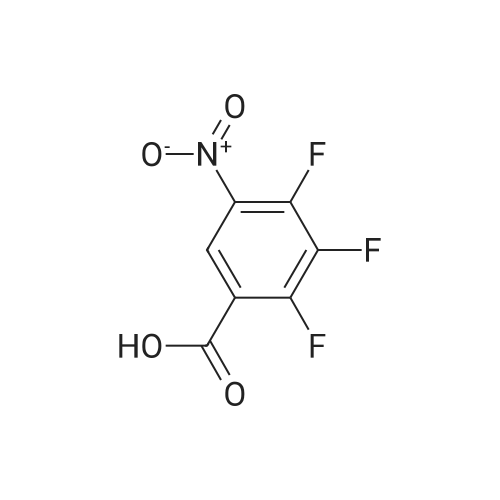
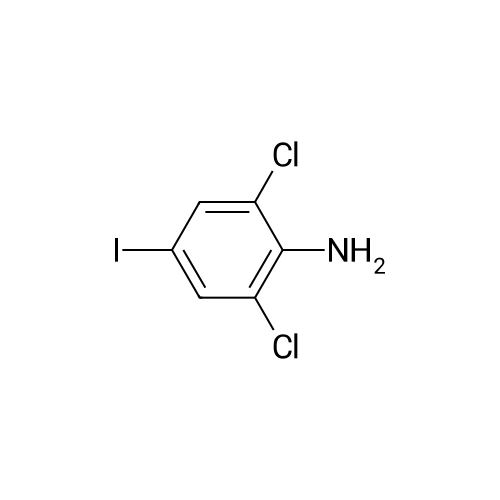
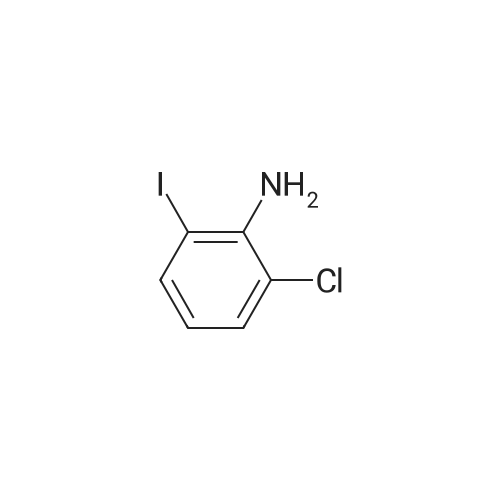
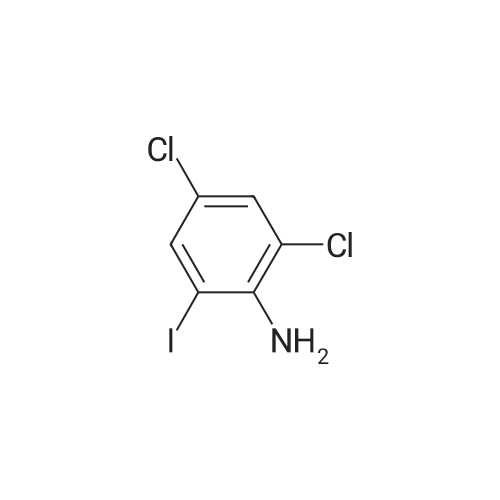
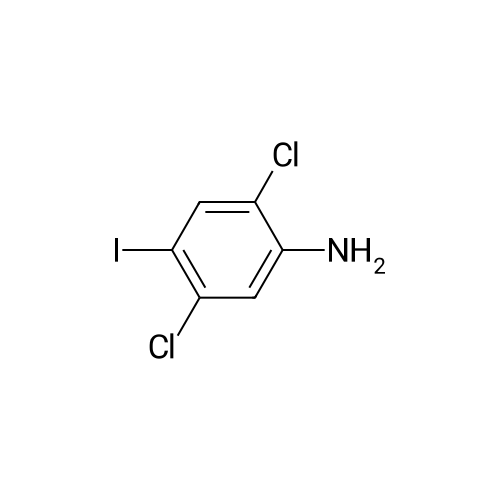
Step b Preparation of 2,4-bis-(2-Chloro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-3-fluoro-5-Nitrobenzoic Acid To a stirring solution comprised of 2-chloro-4-iodoaniline (Lancaster, 98%, 12.33 g, 0.04864 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) at -78 C. under nitrogen was added a 2.0 M lithium diisopropylamide solution in tetrahydrofuran-heptane-ethylbenzene (Aldrich, 35 ml, 0.070 mol) with a syringe. The addition formed a thick suspension. After five minutes of stirring, a solution comprised of <strong>[197520-71-1]5-nitro-2,3,4-trifluorobenzoic acid</strong> (5.00 g, 0.0226 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added with a syringe to give a dark reaction mixture. The cold bath was removed and the reaction mixture stirred for 20 minutes. The cool reaction mixture was poured into ether (600 ml) containing an excess of hydrogen chloride. The red solution instantly turned to a yellow suspension as a precipitate formed. This precipitate was removed by vacuum filtration. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to a red powder (10.5 g). The red powder was triturated with boiling chloroform (800 ml). The triturated solids were collected by vacuum filtration to give an orange powder (2.42 g). The mother liquor from the trituration was concentrated in vacuo to give a red-orange solid (ca. 10 g undried). This solid was loaded onto a flash silica column. Elution with dichloromethane removed some impurities. Continuing elution with 1% methanol in dichloromethane afforede ca. 4 g of a red solid. This red solid was dissolved in hot absolute ethanol (100 ml). The solution was boiled down to 50 ml before dilution to 300 ml with hexanes. This solution was boiled to 150 ml and rediluted to 300 ml with hexanes to produce slight turbidity. The mixture was cooled in the refrigerator for three days, affording a yellow precipitate. The precipitate was collected by vacuum filtration and was dried with suction to afford 0.15 g of a yellow solid; 1% yield; 1H-NMR (400 MHz; DMSO) delta 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, 2H, J=2.0 Hz), 7.61-7.57 (m, 2H), 6.90 (dd, 1 H, J=8.5, 3.9 Hz), 6.84 (dd, 1H, J=8.3, 6.6 Hz); 19F-NMR (376 MHz; DMSO) delta-122.62 (s); MS (APCI+) 692 (6), 691 (8), 690 (31), 689 (10), 688 (55), 171 (47), 130 (100); (APCI-) 691 (4), 690 (12), 689 (14), 688 (70), 687 (32), 686 (100), 506 (50), 453 (97); IR (KBr) 1523 cm-1; Anal. calcd/found for: C19H10Cl2Fl2N3O4 C, 33.17/33.32; H, 1.47/1.73; N, 6.11/5.73; Cl 10.31/10.04; F, 2.76/3.70; I, 36.89134.32. |
| 1% |
With lithium diisopropyl amide; In tetrahydrofuran; tetrahydrofuranheptane-ethylbenzene; ethanol; dichloromethane; |
Step b: Preparation of 2,4-bis-(2-chloro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-3-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid To a stirring solution comprised of 2-chloro-4-iodoaniline (Lancaster, 98 %, 12.33 g, 0.04864 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) at -78 C under nitrogen was added a 2.0 M lithium diisopropylamide solution in tetrahydrofuranheptane-ethylbenzene (Aldrich, 35 ml, 0.070 mol) with a syringe. The addition formed a thick suspension. After five minutes of stirring, a solution comprised of <strong>[197520-71-1]5-nitro-2,3,4-trifluorobenzoic acid</strong> (5.00 g, 0.0226 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added with a syringe to give a dark reaction mixture. The cold bath was removed and the reaction mixture stirred for 20 minutes. The cool reaction mixture was poured into ether (600 ml) containing an excess of hydrogen chloride. The red solution instantly turned to a yellow suspension as a precipitate formed. This precipitate was removed by vacuum filtration. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to a red powder (10.5 g). The red powder was triturated with boiling chloroform (800 ml). The triturated solids were collected by vacuum filtration to give an orange powder (2.42 g). The mother liquor from the trituration was concentrated in vacuo to give a red-orange solid (ca. 10 g undried). This solid was loaded onto a flash silica column. Elution with dichloromethane removed some impurities. Continuing elution with 1 % methanol in dichloromethane afforede ca. 4 g of a red solid. This red solid was dissolved in hot absolute ethanol (100 ml). The solution was boiled down to 50 ml before dilution to 300 ml with hexanes. This solution was boiled to 150 ml and rediluted to 300 ml with hexanes to produce slight turbidity. The mixture was cooled in the refrigerator for three days, affording a yellow precipitate. The precipitate was collected by vacuum filtration and was dried with suction to afford 0.15 g of a yellow solid; 1 % yield; 1H-NMR (400 MHz; DMSO) delta 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, 2H, J=2.0 Hz), 7.61-7.57 (m, 2H), 6.90 (dd, 1H, J=8.5, 3.9 Hz), 6.84 (dd, 1H, J=8.3, 6.6 Hz); 19F-NMR (376 MHz; DMSO) delta -122.62 (s); MS (APCI+) 692 (6), 691 (8), 690 (31), 689 (10), 688 (55), 171 (47), 130 (100); (APCI-) 691 (4), 690 (12), 689 (14), 688 (70), 687 (32), 686 (100), 506 (50), 453 (97); IR (KBr) 1523 cm-1; Anal. calcd/found for: C19H10Cl2FI2N3O4 C, 33.17/33.32; H, 1.47/1.73; N, 6.11/5.73; Cl, 10.31/10.04; F, 2.76/3.70; I, 36.89/34.32. |
| 1% |
With lithium diisopropyl amide; In tetrahydrofuran; tetrahydrofuranheptane-ethylbenzene; ethanol; dichloromethane; |
Step b: Preparation of 2,4-bis-(2-chloro-4-iodo-phenylamino)-3-fluoro-5-nitrobenzoic acid To a stirring solution comprised of 2-chloro-4-iodoaniline (Lancaster, 98 %, 12.33 g, 0.04864 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (20 ml) at -78 C under nitrogen was added a 2.0 M lithium diisopropylamide solution in tetrahydrofuranheptane-ethylbenzene (Aldrich, 35 ml, 0.070 mol) with a syringe. The addition formed a thick suspension. After five minutes of stirring, a solution comprised of <strong>[197520-71-1]5-nitro-2,3,4-trifluorobenzoic acid</strong> (5.00 g, 0.0226 mol) in tetrahydrofuran (30 ml) was added with a syringe to give a dark reaction mixture. The cold bath was removed and the reaction mixture stirred for 20 minutes. The cool reaction mixture was poured into ether (600 ml) containing an excess of hydrogen chloride. The red solution instantly turned to a yellow suspension as a precipitate formed. This precipitate was removed by vacuum filtration. The filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to a red powder (10.5 g). The red powder was triturated with boiling chloroform (800 ml). The triturated solids were collected by vacuum filtration to give an orange powder (2.42 g). The mother liquor from the trituration was concentrated in vacuo to give a red-orange solid (ca. 10 g undried). This solid was loaded onto a flash silica column. Elution with dichloromethane removed some impurities. Continuing elution with 1 % methanol in dichloromethane afforede ca. 4 g of a red solid. This red solid was dissolved in hot absolute ethanol (100 ml). The solution was boiled down to 50 ml before dilution to 300 ml with hexanes. This solution was boiled to 150 ml and rediluted to 300 ml with hexanes to produce slight turbidity. The mixture was cooled in the refrigerator for three days, affording a yellow precipitate. The precipitate was collected by vacuum filtration and was dried with suction to afford 0.15 g of a yellow solid; 1 % yield; 1H-NMR (400 MHz; DMSO) delta 8.94 (s, 1H), 8.55 (s, 1H), 7.79 (d, 2H, J=2.0 Hz), 7.61-7.57 (m, 2H), 6.90 (dd, 1H, J=8.5, 3.9 Hz), 6.84 (dd, 1H, J=8.3, 6.6 Hz); 19F-NMR (376 MHz; DMSO) delta -122.62 (s); MS (APCI+) 692 (6), 691 (8), 690 (31), 689 (10), 688 (55), 171 (47), 130 (100); (APCI-) 691 (4), 690 (12), 689 (14), 688 (70), 687 (32), 686 (100), 506 (50), 453 (97); IR (KBr) 1523 cm-1; Anal. calcd/found for: C19H10Cl2Fl2N3O4 C, 33.17/33.32; H, 1.47/1.73; N, 6.11/5.73; Cl, 10.31/10.04; F, 2.76/3.70; I, 36.89/34.32. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science













 HazMat Fee +
HazMat Fee +

 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping