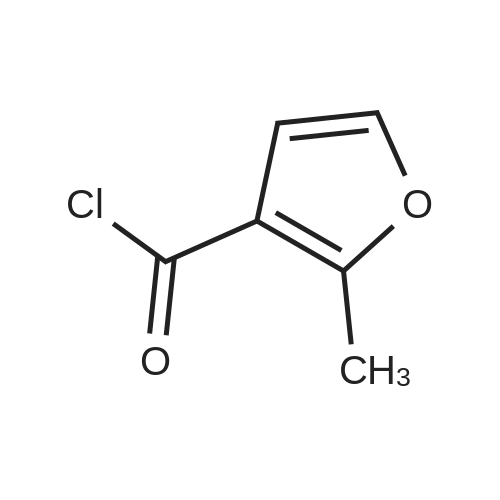
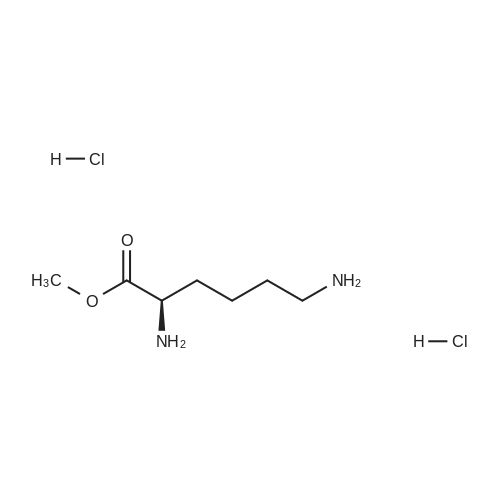
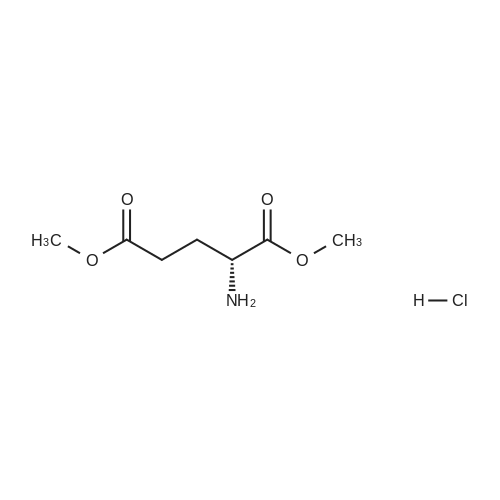
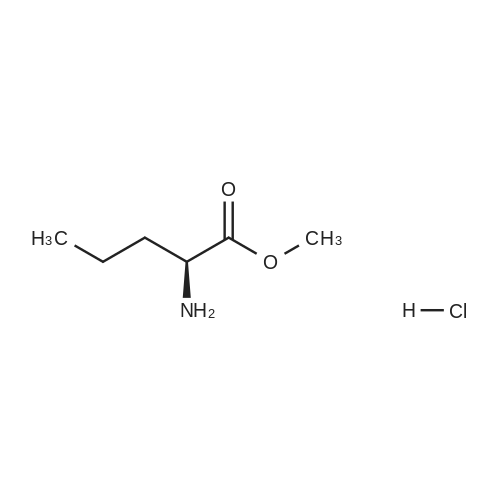
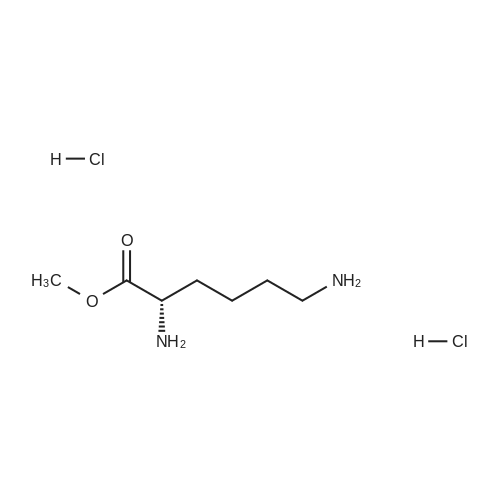
N-Salicyloyl acidic amino acids are a promising colon-specific promoiety of riluzole against rat colitis
Kim, Jaejeong
;
Kang, Changyu
;
Jung, Yunjin
J. Pharm. Investig.,2024.
DOI:
10.1007/s40005-024-00710-w
More
Abstract: Purpose: In our previous study, riluzole (RLZ) azo-linked to salicylic acid (RAS) was prepared as a colon-targeted RLZ prodrug against rat colitis. However, RAS was not a satisfactory colon-targeted prodrug because of its non-negligible systemic absorption, leading to low colonic delivery efficiency and the ability to limit the systemic absorption of RLZ. This study aimed to improve the colon specificity and anticolitic activity of RAS.
Methods: Salicylic acid (SA) was conjugated with the acidic amino acids aspartic acid (Asp) and glutamic acid (Glu) and subsequently azo-coupled with RLZ to yield Asp-conjugated RAS (RAS-Asp) and Glu-conjugated RAS (RAS-Glu).
Results: Amino acid-conjugated RAS lowered the distribution coefficient and cell permeability of RAS while exhibiting a release profile of RLZ similar to that of RAS in the cecal contents. Upon oral gavage, amino acid-conjugated RAS delivered a larger amount of RLZ to the cecum than RAS. The ability of amino acid-conjugated RAS to limit the systemic absorption of RLZ was greater than that of RAS. No significant differences were observed in the colon-specific performance between RAS-Asp and RAS-Glu. In a DNBS-induced rat colitis model, amino acid-conjugated RAS was more effective than RAS in ameliorating colonic damage and inflammation and modulating the anti-inflammatory GSK3β-IL-10 pathway in the inflamed colon, without a significant difference between RAS-Asp and RAS-Glu.
Conclusion: Conjugation of acidic amino acids with RAS improved the colon specificity, anticolitic activity, and safety of RAS. N-Salicyloyl acidic amino acids may act as high-performance colon-specific promiety for a candidate drug modifiable to a colon-targeted prodrug with an azo bond as a colon-specific link.
Keywords:
Riluzole ;
Colon-targeted prodrug ;
Colitis ;
Acidic amino acids ;
High performance colon-specific promoiety
Purchased from AmBeed:
23150-65-4 ;
1744-22-5 ;
32213-95-9 ;
530-62-1

Colon-Targeted Poly (ADP-Ribose) Polymerase Inhibitors Synergize Therapeutic Effects of Mesalazine Against Rat Colitis Induced by 2, 4-Dinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid
Kang, Changyu
;
Kim, Jaejeong
;
Jeong, Yeonhee
, et al.
Pharmaceutics,2024,16(12):1546.
DOI:
10.3390/pharmaceutics16121546
More
Abstract: Background/Objectives: In addition to oncological applications, poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors have potential as anti-inflammatory agents. Colon-targeted delivery of PARP inhibitors has been evaluated as a pharmaceutical strategy to enhance their safety and therapeutic efficacy against gut inflammation. Methods: Colon-targeted PARP inhibitors 5-aminoisoquinoline (5-AIQ) and 3-aminobenzamide (3-AB) were designed and synthesized by azo coupling with salicylic acid (SA), yielding 5-AIQ azo-linked with SA (AQSA) and 3-AB azo-linked with SA (ABSA). Additional conjugation of AQSA with acidic amino acids yielded glutamic acid-conjugated AQSA (AQSA-Glu) and aspartic acid-conjugated AQSA, which further increased the hydrophilicity of AQSA. Results: The distribution coefficients of PARP inhibitors were lowered by chemical modifications, which correlated well with drug permeability via the Caco-2 cell monolayer. All derivatives were effectively converted to their corresponding PARP inhibitors in the cecal contents. Compared with observations in the oral administration of PARP inhibitors, AQSA-Glu and ABSA resulted in the accumulation of much greater amounts of each PARP inhibitor in the cecum. ABSA accumulated mesalazine (5-ASA) in the cecum to a similar extent as sulfasalazine (SSZ), a colon-targeted 5-ASA prodrug. In the DNBS-induced rat colitis model, AQSA-Glu enhanced the anticolitic potency of 5-AIQ. Furthermore, ABSA was more effective against rat colitis than SSZ or AQSA-Glu, and the anticolitic effects of AQSA-Glu were augmented by combined treatment with a colon-targeted 5-ASA prodrug. In addition, the colon-targeted delivery of PARP inhibitors substantially reduced their systemic absorption. Conclusions: Colon-targeted PARP inhibitors may improve the therapeutic and toxicological properties of inhibitors and synergize the anticolitic effects of 5-ASA.
Keywords:
poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor ;
colon-targeted drug delivery ;
colitis ;
mesalazine ;
prodrug
Purchased from AmBeed:
23150-65-4 ;
32213-95-9 ;
15722-48-2 ;
530-62-1
 Polymerase Inhibitors Synergize Therapeutic Effects of Mesalazine Against Rat Colitis Induced by 2, 4-Dinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid.png)

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping




 Polymerase Inhibitors Synergize Therapeutic Effects of Mesalazine Against Rat Colitis Induced by 2, 4-Dinitrobenzenesulfonic Acid.png)