Alternatived Products of [ 1675-54-3 ]
Product Details of [ 1675-54-3 ]
| CAS No. : | 1675-54-3 |
MDL No. : | MFCD00080480 |
| Formula : |
C21H24O4
|
Boiling Point : |
- |
| Linear Structure Formula : | (CH2OCH)CH2OC6H4C(CH3)2C6H4OCH2(CHOCH2) |
InChI Key : | LCFVJGUPQDGYKZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| M.W : |
340.41
|
Pubchem ID : | 2286 |
| Synonyms : |
BADGE;NSC 5022;DGEBA
|
Chemical Name : | 2,2-Bis(4-glycidyloxyphenyl)propane |
Application In Synthesis of [ 1675-54-3 ]
* All experimental methods are cited from the reference, please refer to the original source for details. We do not guarantee the accuracy of the content in the reference.
- Downstream synthetic route of [ 1675-54-3 ]
- 1
-
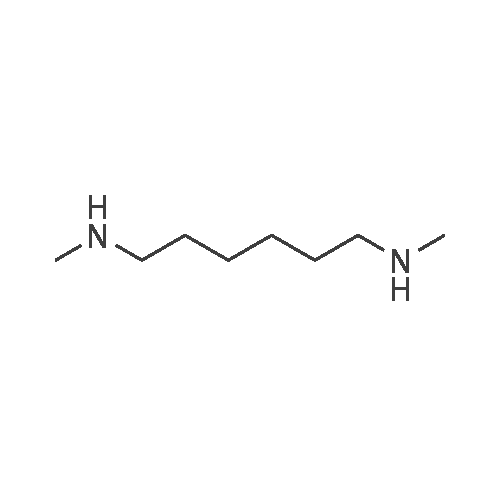 [ 13093-04-4 ]
[ 13093-04-4 ]

-
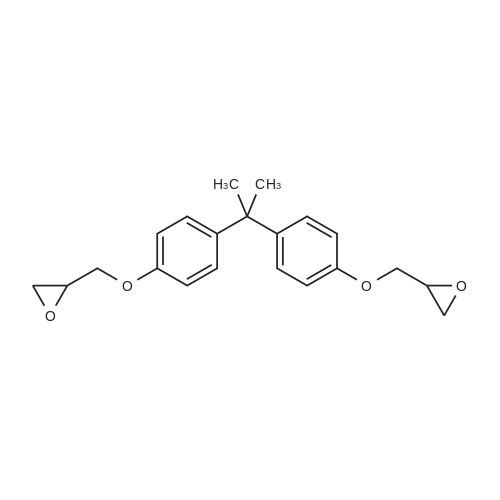 [ 1675-54-3 ]
[ 1675-54-3 ]

-
 [ 30215-97-5 ]
[ 30215-97-5 ]
- 2
-
 [ 4809-35-2 ]
[ 4809-35-2 ]

-
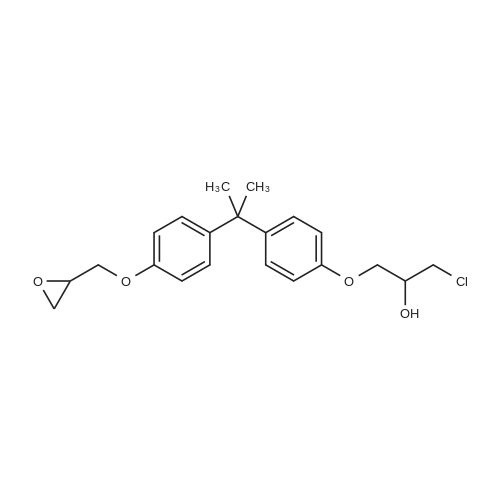 [ 13836-48-1 ]
[ 13836-48-1 ]

-
C21H25ClO4
[ No CAS ]

-
C23H27ClO5
[ No CAS ]

-
C23H28O6
[ No CAS ]

-
C24H32O7
[ No CAS ]

-
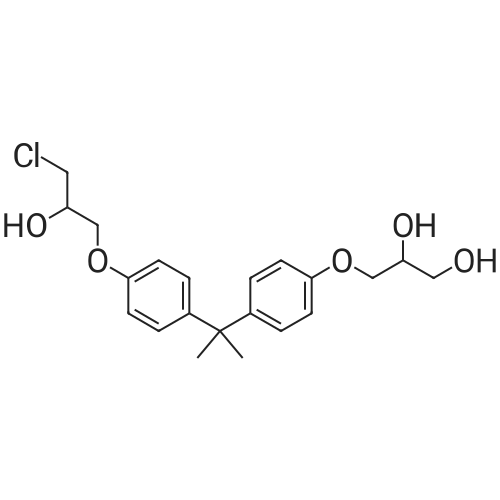 [ 227947-06-0 ]
[ 227947-06-0 ]

-
C24H32O6
[ No CAS ]

-
 [ 1675-54-3 ]
[ 1675-54-3 ]

-
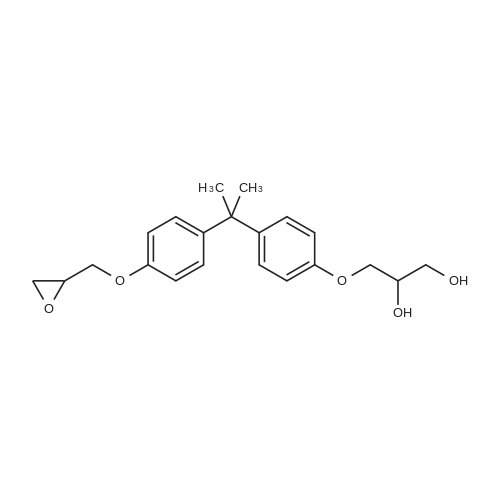 [ 76002-91-0 ]
[ 76002-91-0 ]
| Yield | Reaction Conditions | Operation in experiment |
|
With sodium hydroxide; In 1-methoxy-2-propanol; water; at 25 - 52℃; for 2.5h; |
E. Conversion of Bisphenol A Bis(α-chlorohydrin) Intermediate to Bisphenol A Diglycidyl Ether Epoxy Resin; [00279] In this part of Example 1, a 250-ml, four-necked, glass reactor equipped with a cooling condenser, a thermometer, a magnetic stirrer, an addition funnel for liquids, and a heating lamp with a thermo-controller was employed. Into the reactor was transferred crude bis(α-chlorohydrin) derivative of bisphenol A prepared via a chloride substitution process and described in Experiment C2 of Example 2 of U.S. Pat. No. 6,534,621, incorporated herein by reference. To the reactor was also added 100 g of 1-methoxy-2-hydroxypropane as solvent. At ambient temperature, 12 g of 50% aqueous NaOH solution (0.15 mole) was added slowly to the mixture over a period of 30 minutes, after which the mixture was allowed to react for about an additional 30 minutes in order to neutralize unreacted HCl dissolved in the mixture. [00280] After removing the resulting precipitated salt by filtration, the resultant solution was transferred into another 250-mL, four-necked, glass reactor equipped with a cooling condenser, a thermometer, a magnetic stirrer, an addition funnel for liquids, and a heating lamp with a thermo-controller. The solution was heated to 50-52 C. Using the addition funnel, 12 g of 50% aqueous NaOH solution (0.15 mole) was added slowly to the heated solution over a period of 60 minutes at 50-52 C., after which time the resulting reaction mixture was allowed to react for about an additional 60 minutes at 50-52 C. GC analysis of the resultant product indicated that greater than 90% of the bis(α-chlorohydrin) derivative was converted into bisphenol A diglycidyl ether (BADGE) as identified by GC elution time comparison with an authentic commercial sample. The epoxy product was dissolved into 150 mL methyl ethyl ketone-toluene mixture (50:50, volume:volume) and was washed twice with 50 mL portions of water. The organic phase was separated and concentrated by rotary evaporation at 90-95 C. and less than 15 mmHg, yielding 13 g of epoxy resin having an epoxy content of 20.33% and an epoxy equivalent weight of 209. This reaction product was analyzed by high pressure liquid chromatography (HPLC)/mass spectrometry (MS) and the analysis of the major components is shown in Table II below. |
Categories

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping











