|
|
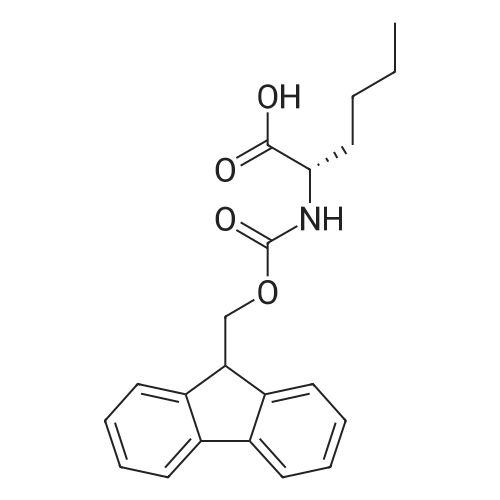
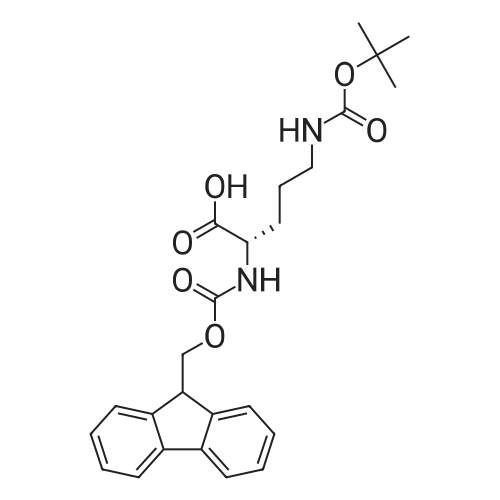
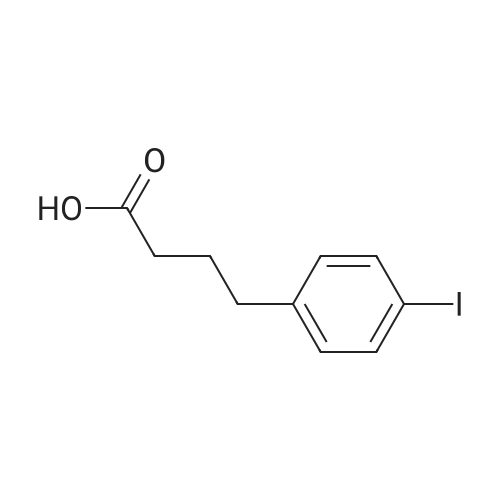
Fmoc-Lys(ivDde)-Wang resin (0.3 mmol, 0.61 mmol/g loading) was suspended in DMF for 30 mm. Fmoc was then removed by treating the resin with 20% piperidine in DMF (3 x 8 mm). The isocyanate derivative of di-t-butyl ester of glutamate (3 eq.) was prepared according to literatureprocedures,17 and added to the lysine-immobilized resin and reacted for 16 h. After washing the resinwith DMF, the ivDde-protecting group was removed with 2% hydrazine in DMF (5 x 5 mi. Fmoc-2- Nal-OH was then coupled to the side chain of Lys followed by Fmoc-tranexamic acid, FmocLys(ivDde)-OH, and Fmoc-Gly-OH via solid-phase peptide synthesis using Fmoc-based chemistry. Allcouplings were carried out in DMF using Fmoc-protected amino acid (3 eq.), HBTU (3 eq.), HOBT (3eq.), and DIEA (8 eq.). Afterwards, elongation was continued with the addition of <strong>[27913-58-2]4-<strong>[27913-58-2](p-iodophenyl)butyric acid</strong></strong> (for HTK03024), 4-(p-chlorophenyl)butyric acid (for HTK03055), 4-phenylbutyric acid (for HTK03056), 4-(p-bromophenyl)butyric acid (for HTK03058), 3-phenyipropanoic acid (for HTK03082), 4-(p-fluorophenyl)butyric acid (for HTK03085), 4-(p-methoxyphenyl)butyric acid(for HTK03086), 4-(p-(t-butyloxycarbonyl)aminophenyl)butyric acid (for HTK03087), 4-(p-nitrophenyl)butyric acid (for HTK03089), or 4-(p-tolyl)butyric acid (for HTKO3O9O) were coupled to thesame peptide-bound resin using Fmoc-based chemistry. After selective removal of the ivDdeprotecting group with 2% hydrazine in DMF (5 x 5 mm), the chelator DOTA was then coupled to theside chain of Lys to give the precursors. The peptide was then deprotected and simultaneously cleaved from the resin by treatingwith 95/5 trifluoroacetic acid (TFA)/triisopropylsilane (TIS) for 2 h at room temperature. After filtration,the peptide was precipitated by the addition of cold diethyl ether to the TFA solution. The crude peptide was purified by HPLC using the semi-preparative column. The eluates containing the desired peptidewere collected, pooled, and lyophilized. For HTK03024, the HPLC conditions were 37% acetonitrile inwater with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retention time was 8.8 mi ESI-MS: calculated[M+H] for HTK03024 C67H96N120191 1499.6; found [M+H] 1499.6. For HTK03055, the HPLCconditions were 35% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retentiontime was 9.7 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03055 C67H96N12019C1 1407.7; found [M+H]1407.7. For HTK03056, the HPLC conditions were 0-80% acetonitrile in waterwith 0.1% TFA ata flowrate of 4.5 mL/min in 20 mm. The retention time was 13.4 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] forHTK03056 C67H97N12019 1373.7; found [M+H] 1373.8. For HTK03058, the HPLC conditions were 0-80% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min in 20 mm. The retention time was13.4 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03058 C67H96N12O19Br 1451.6; found [M+H] 1451.6. ForHTK03082, the HPLC conditions were 31% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5mL/min. The retention time was 11.1 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03082 C66H95N120191359.7; found [M+H] 1359.9. For HTK03085, the HPLC conditions were 34% acetonitrile in waterwith0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retention time was 9.0 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] forHTK03085 C67H96N12019F 1391.7; found [M+H] 1391.9. For HTK03086, the HPLC conditions were33% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retention time was 9.1 mm.ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03086 C68H99N12020 1403.7; found [M+H] 1404.1. For HTK03087,the HPLC conditions were 23% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA ata flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. Theretention time was 13.9 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03087 C67H98N13019 1388.7; found[M+H] 1389.0. For HTK03089, the HPLC conditions were 33% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA ataflow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retention time was 10.6 mi ESI-MS: calculated [M+H] for HTK03089C67H96N13021 1418.7; found [M+H] 1419.0. For HTKO3O9O, the HPLC conditions were 35% acetonitrile in water with 0.1% TFA at a flow rate of 4.5 mL/min. The retention time was 9.1 mm. ESI-MS:calculated [M+H] for HTKO3O9O C68H99N12019 1387.7; found [M+H] 1387.9. |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping