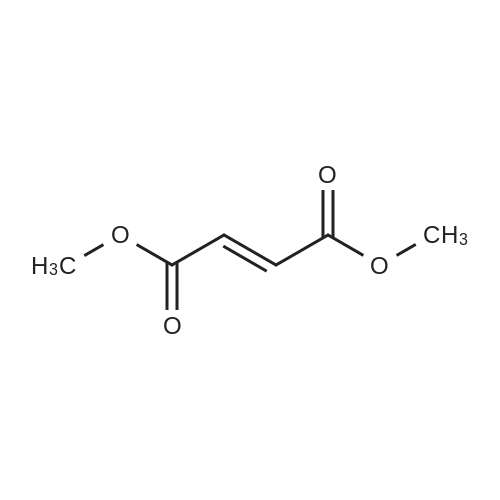
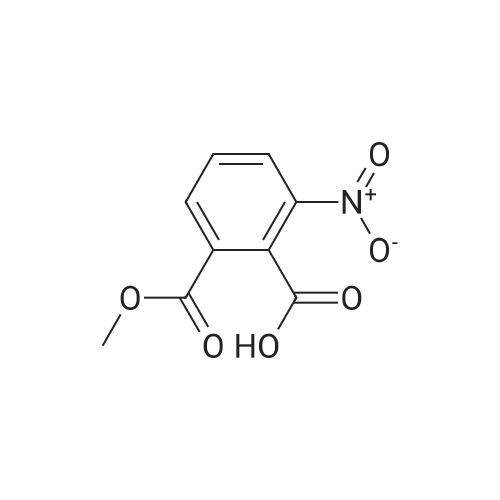
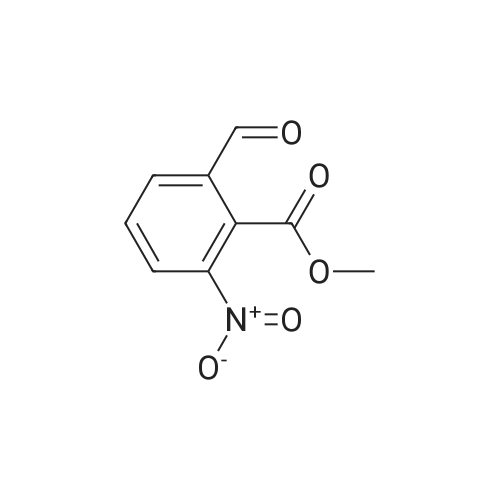
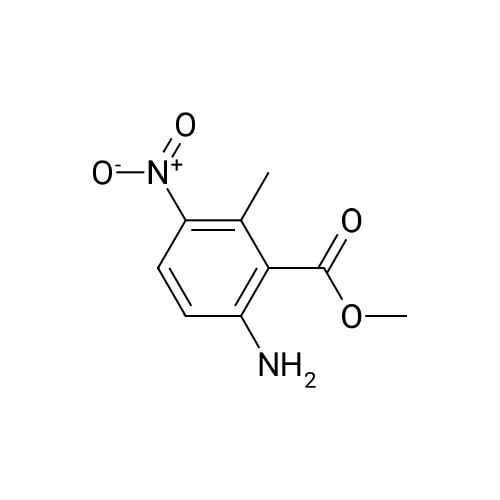
| 86% |
|
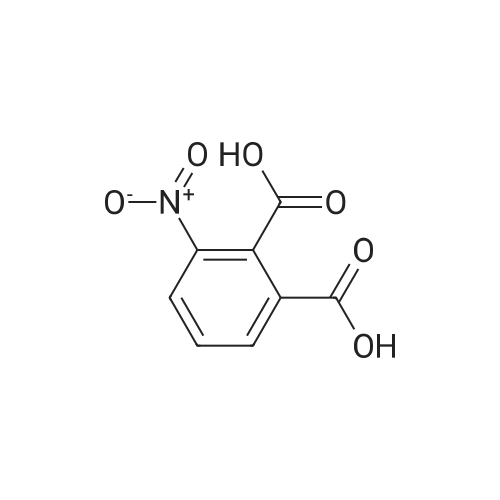
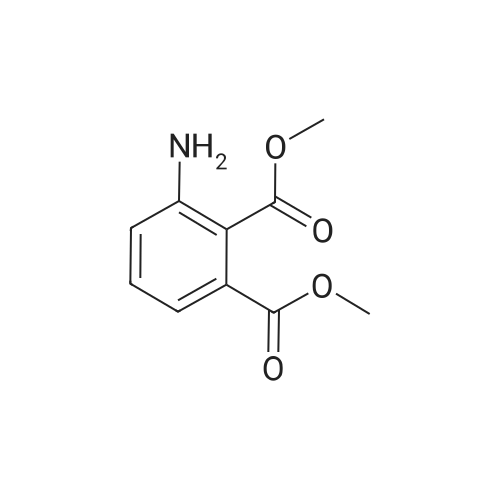
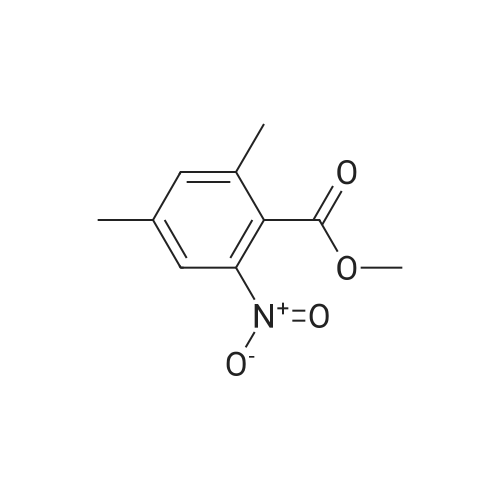
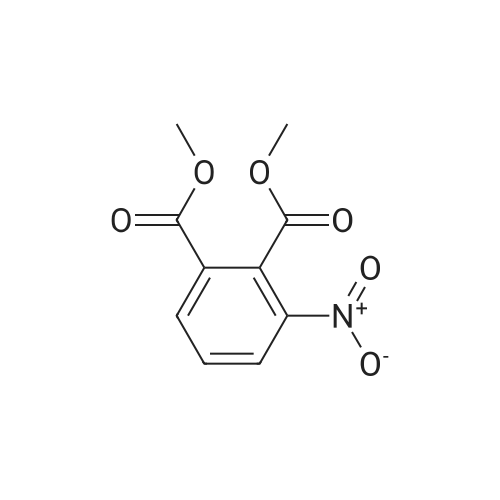
5.40.2 3-Aminophthalic Acid Dimethyl Ester A mixture of 3:1 ethanol-conc. HCl (200 mL) was cooled to 0 C. and then 3-nitrophthalic acid dimethyl ester (15.0 g, 62.8 mmol) was added. Maintaining the cooling, tin chloride (70.8 g, 314 mmol) was added portionwise, over a period of 15 minutes. Following completion of the addition, the cooling bath was removed, and stirring proceeded at room temperature. After 2 hours, the mixture was neutralized by the addition of solid sodium bicarbonate, and the resulting mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3×150 mL) and the combined extracts were washed with water (5×250 mL), were dried (MgSO4) and evaporated, providing 11.3 g of the product as a yellow oil in 86% yield: 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 5.20 (br, 2H), 6.78 (dd, J=8.5 Hz, J=1.0 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (dd, 1H, J=7.3 Hz, J=1.0 Hz, 1H), 7.24 (t, J=7.8 Hz, 1H). |
| 86% |
|
Step 2:[163] A mixture of 3:1 ethanol-conc. HCl (200 mL) was cooled to 0 0C and then 3- nitrophthalic acid dimethyl ester (15.0 g, 62.8 mmol) was added. Maintaining the cooling, tin (II) chloride (70.8 g, 314 mmol) was added portionwise, over a period of 15 min. Following completion of the addition, the cooling bath was removed and stirring proceeded at room temperature. After 2 h, the mixture was neutralized by the addition of solid sodium bicarbonate, and the resulting mixture was extracted with ethyl acetate (3 x 150 mL) and the combined extracts were washed with water (5 x 250 mL), were dried (MgSO4) and evaporated, providing 11.3 g of 3-aminophthalic acid dimethyl ester as a yellow oil, in 86% yield; 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ 3.84 (s, 3H), 3.86 (s, 3H), 5.20 (br, 2H), 6.78 (dd, J = 8.5 Hz, J = 1.0 Hz, IH), 6.90 (dd, IH, J = 7.3 Hz, J = 1.0 Hz, IH), 7.24 (t, J = 7.8 Hz, IH). |
| 83% |
With hydrogenchloride; In methanol; water; |
REFERENCE EXAMPLE 102 Dimethyl 3-aminophthalate Dimethyl 3-nitrophthalate (18.0 g, 75.2 mmol) obtained in Reference Example 101 was dissolved in a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid (50.0 ml) water (250 ml) and methanol (25.0 ml), and an excess of zinc powder was added in portions. After completion of the reaction, the reaction mixture was filtered, and the filtrate was made basic with 25% aqueous ammonium hydroxide, and extracted with ethyl acetate. After the extract was washed with water and dried (MgSO4), the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was subjected to a column chromatography on a silica gel eluding with n-hexane-ethyl acetate (10:1, v/v) to give the title compound (13.1 g, 83%) as an oil. 1H-NMR (CDCl3) δ: 3.85 (3H, s), 3.86 (3H, s), 5.20 (2H, bs), 6.78 (1H, dd, J=8.4, 1.2 Hz), 6.90 (1H, dd, J=7.4, 0.8 Hz), 7.24 (1H, d, J=8.0 Hz). |
| 18.1 g (87%) |
With hydrogen;palladium-carbon; In ethyl acetate; |
Methyl-3-amino-2-(methoxycarbonyl)benzoate To a solution of methyl-2-(methoxycarbonyl)-3-nitrobenzoate (23.8 g, 99.51 mmol) in ethyl acetate (200 ml) was added 10% Pd/C (1.8 g). The mixture was hydrogenated under 50 psi of hydrogen for 3 hours in a Parr Type Shaker. The mixture was filtered through Celite and the filtrate was concentrated in vacuo to yield an oil. The crude product was purified by flash chromatography (dichloromethane/ethyl acetate 95 to 5) to afford 18.1 g (87%) of the product as a brown oil: 1H NMR (CDCl3) δ7.22 (t, J=7.6 Hz, 1H), 6.90 (d, J=7.2 Hz, 1H), 6.79 (d, J=8.7 Hz), 5.07 (b, 2H), 3.85 (s, 3H), 3.83 (s, 3H). |
|
With hydrogen;palladium 10% on activated carbon; In methanol; at 20℃; under 2327.23 Torr; |
Preparation of 3-amino-phthalic Acid Dimethyl Ester, 3 The compound 2 (205 g, 1.0 mol) was dissolved in 2 L of MeOH. Catalytic 10% Pd/C was added and the solution was hydrogenated under H2 (45 psi) on a Parr hydrogenation apparatus at room temperature overnight. Filtered through celite and evaporated to give a quantitative yield of 3-amino-phthalic acid dimethyl ester, 3. 1H NMR (300 MHz, DMSO-d6): 7.26 (t, J=7.33 Hz, 1H), 6.94 (d, J=8.34 Hz, 1H), 6.77 (d, J=8.33 Hz, 1H), 6.12 (s, 2H), 3.77 (s, 3H), 3.76 (s, 3H). 13C NMR: 51.51, 51.77, 110.50, 115.16, 118.56, 131.26, 133.16, 148.28, 167.12, 168.11. |
|
With palladium 10% on activated carbon; hydrogen; In acetone; at 20℃; under 3102.97 Torr; for 5h; |
Dissolve Compound 1 (500mg) in acetone (30mL) solution, transfer to a hydrogenation reaction flask, add Pd / C (40mg, 10%), build a hydrogenation device, and react at 60psi for 5h at room temperature. , Remove the device, remove Pd / C by suction filtration, condense at low temperature by rotary evaporation, extract with ethyl acetate (30mLx3), combine the organic layers, wash once with saturated brine, add anhydrous magnesium sulfate to dry, and dry by suction filtration to obtain crude product. Column chromatography to obtain intermediate 2 |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping