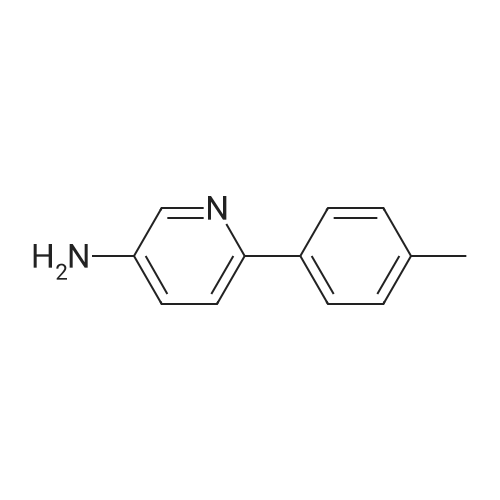
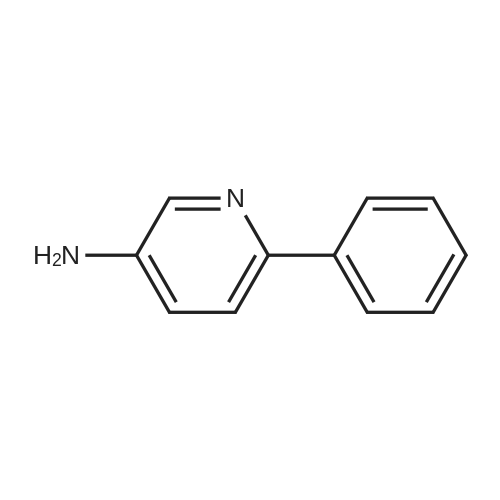
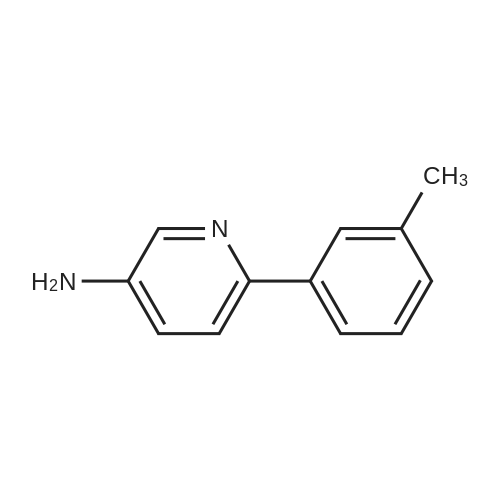
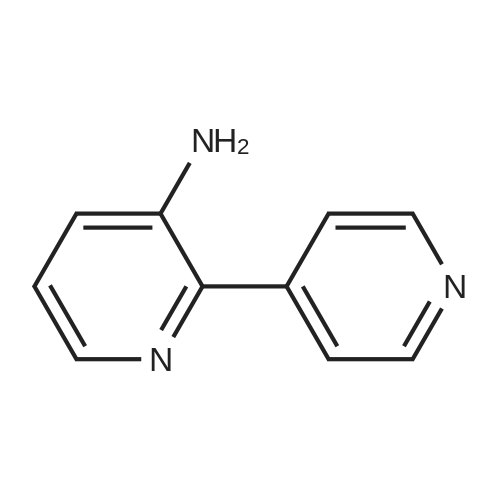
| 97% |
With sodium carbonate; benzaldehyde; triphenylphosphine;palladium diacetate; In water; toluene; |
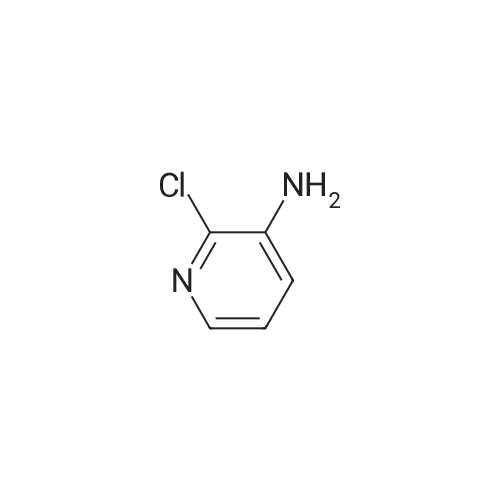
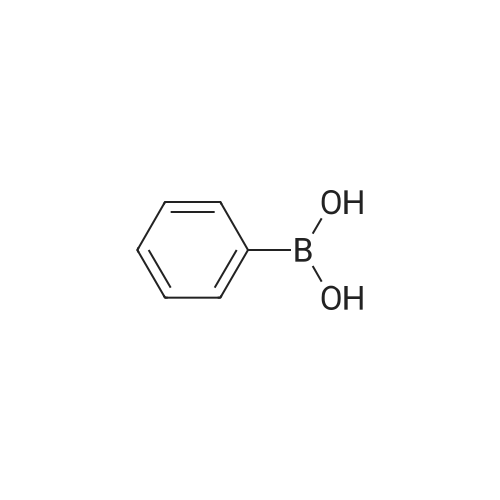
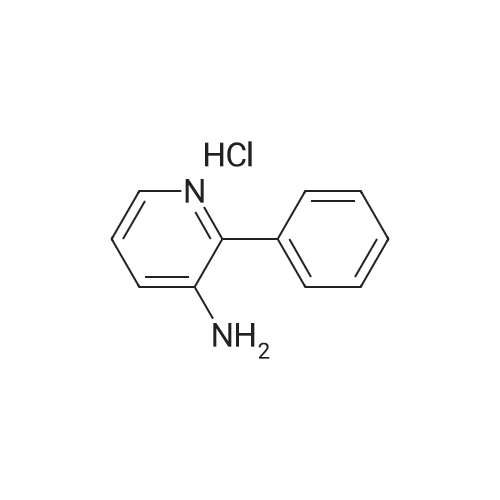
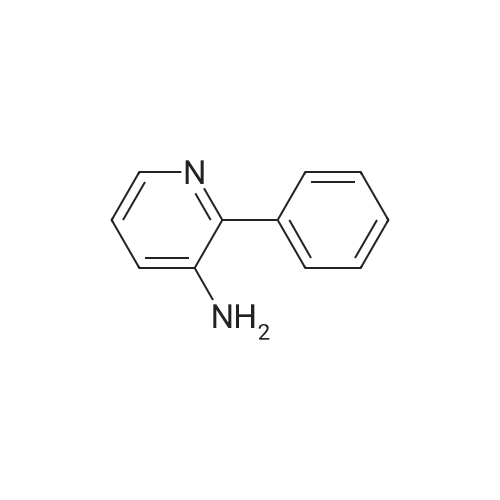
A solution of palladium acetate (224.5 mg, 1.00 mmol) and triphenylphosphine (1.05 g, 4.00 mmol) in toluene (1000 mL) was stirred at room temperature for 15 minutes. Phenylboronic acid (114 g, 935 mmol), 2-chloro-3-aminopyridine (100 g, 778 mmol), benzaldehyde (83.4 g, 786 mmol), and toluene (500 mL) were then added followed by a solution of sodium carbonate (200 g, 1.89 mol) in water (1500 mL). The mixture was heated to reflux for 18 hours, cooled to room temperature, and the layers were separated. The organic layer was washed with water (500 mL) and 2.5M aqueous hydrochloric acid was added (630 mL). The aqueous layer was separated and washed with toluene (300 mL). The pH was adjusted to 12-13 using 50% aqueous sodium hydroxide and the mixture was extracted with methyl-tert-butyl ether (500 mL). The organic layer was concentrated and the product was crystallized from diisopropyl ether to afford 2-phenyl-3-aminopyridine (128 g, 97% yield). M. p.=67-68 C. 1H NMR (300 MHz, CDCl3) δ3.88 (bs, 2), 7.02-7.11 (m, 2). 7.28-7.53 (m, 3), 7.67-7.71 (m, 2), 8.,13-8.16 (m, 1). 13C NMR (100 MHz, CDCl3) δ122.57, 122.96, 128.14, 128.38, 128.72, 138.54, 139.86, 139.93, 144.93. |
| 88% |
With potassium phosphate; tetrabutylammomium bromide; In water; at 90℃; for 6h;Green chemistry; |
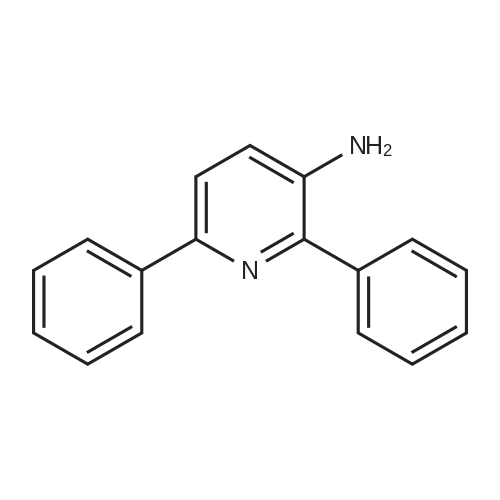
General procedure: To a 10-mL reaction vial, heteroaryl halide (1.0 mmol), boronic acid (1.2 mmol), K3PO4 (2.0 mmol), tetra-butylammonium bromide (TBAB) (0.5 mmol), and 4 (0.1 mol %) in water (3.5 mL) were added. The reaction mixture was stirred at 85 C and the reaction progress was monitored by GC-MS analysis. After completion of the reaction, it was diluted with H2O and CH2Cl2. The organic layer was separated from mixture, the dried organic layer over MgSO4, and evaporated under reduced pressure. The crude reaction product was purified using column chromatography on silica-gel to afford the corresponding product with isolated yield up to 98%. |
| 71% |
|
General procedure: 3-Amino-2-chloropyridine (0.5g, 3.9mmol), phenylboronic acid (0.47 g, 3.9 mmol), and bis(triphenylphosphine)palladium dichloride (0.137 g, 0.195 mmol) were added to 1,4-dioxane (20ml). Under nitrogen atmosphere the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 30 minutes. 1M aqueous sodium carbonate (8 ml) was poured in, and the temperature was raised to 80C. After the reaction at 80C for 8 hours, the mixture was distilled off under reduced pressure. The residue was extracted with addition of ethyl acetate and water. The impurities were filtered off from the organic layer, and the solvent was distilled off under reduced pressure. The purification by column chromatography gave the title compound (0.47 g, 71.0% yield). |

 Chemistry
Chemistry
 Pharmaceutical Intermediates
Pharmaceutical Intermediates
 Inhibitors/Agonists
Inhibitors/Agonists
 Material Science
Material Science














 For Research Only
For Research Only
 120K+ Compounds
120K+ Compounds
 Competitive Price
Competitive Price
 1-2 Day Shipping
1-2 Day Shipping