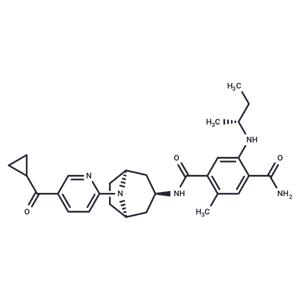
| Name | XL888 |
| Description | XL888 is an ATP-competitive inhibitor of Hsp90 ( IC50: 24 nM). Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is a chaperone that maintains the functionality of client proteins involved in cell proliferation, cell cycling, and apoptosis. Through this action, specific client proteins are degraded, resulting in cell cycle arrest or apoptosis. XL888 is orally bioavailable and shows efficacy in tumor regression in gastric carcinoma and melanoma xenografts in mice. |
| Cell Research | Cells are plated at a density of 2×105 per mL and left to grow overnight before being treated with increasing concentrations of XL888. After incubation with XL888 for 3 days, Methylthiazolyldiphenyl-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assays are performed.(Only for Reference) |
| Kinase Assay | The PTP1B enzymatic assay, the total volume of 100 μL per well contains15 nM recombinant PTP1B protein, 2 mM p-nitrophenylphosphonic acid (pNPP), 1 mM dithiothreitol and 1 mM EDTA (pH 6.5). After 30 min incubation at 37℃, end the reaction by addition of 2.5 M NaOH. The hydrolysis product, pNP, is detected at the absorbance at 405 nm. |
| In vitro | XL888 induces HER2 degradation in NCI-N87 cells with IC50 of 56 nM. XL888 inhibits the proliferation of HER2 over-expressed NCI-N87, HER2 over-expressed BT-474, HER2 over-expressed MDA-MB-453, MET mutated MKN45, B-Raf mutated Colo-205, B-Raf mutated SK-MEL-28, EGFR mutated HN5, EGFR mutated NCI-H1975, PI3K mutated MCF7, and K-Ras mutated A549 with IC50 of 21.8, 0.1, 16.0, 45.5, 11.6, 0.3, 5.5, 0.7, 4.1 and 4.3 nM. [1] XL888 leads to dose-dependent decreases in the growth of vemurafenib-naive and vemurafenib-resistant melanoma cell lines and melanoma cell lines with intrinsic resistance with IC50 of all around 0.1 μM. The growth inhibitory effects of XL888 are associated with induction of either a G1-phase cell-cycle arrest (WM164, M229, M229R, M249, M249R, 1205Lu, and WM39 cell lines) or a G2-M phase cell-cycle arrest (WM164R, 1205LuR, and RPMI 7951 cell lines). XL888 (300 nmol) induces high levels ( > 66%) of apoptosis, and loss of mitochondrial membrane potential (TMRM) in these cell lines. The cytotoxic effects of XL888 are durable with no signs of colony formation observed in any of the cell lines even cultured up to 4 weeks. XL888 treatment (300 nM, 48 hours) leads to the degradation of IGF1R, PDGFRβ, ARAF, CRAF, and cyclin D1 and the inhibition of AKT, ERK, and S6 signaling in all of the cell lines with acquired BRAF inhibitor resistance. treatment of cell lines that are naive, intrinsically resistant, and with acquired vemurafenib resistance. Treatment with XL888 (300 nM) leads to robust time-dependent increases in the expression of HSP70 isoform 1. XL888 (48 hours, 300 nM) treatment increases the expression of BIM-EL, BIM-L, and BIM-S expression in the M229R, 1205LuR, RPMI7951, and WM39 cell lines, induces expression of BIM-L and BIM-S in the WM164R cell line, and BIM-EL in the M249R cell line. [2] |
| In vivo | XL888 (100 mg/kg) significantly induces the regression of, or growth inhibition (50%) of established M229R and 1205LuR xenografts in SCID mice. 15 days of XL888 treatment showes a robust (8.6-fold) increase in intratumoral HSP70 expression compared with controls. XL888 treatment is noted to be proapoptotic in vivo and leads to increased TUNEL staining in M229R xenografts associated with increased expression of BIM and decreased expression of Mcl-1. [2] |
| Storage | Powder: -20°C for 3 years | In solvent: -80°C for 1 year | Shipping with blue ice. |
| Solubility Information | DMSO : 55 mg/mL (109.2 mM)
|
| Keywords | Heat shock proteins | XL888 | XL-888 | HSP | Inhibitor | XL 888 | inhibit |
| Inhibitors Related | Ethoxyquin | SNX0723 | Tamoxifen | DN401 | SNX2112 | Ganetespib | Teprenone | Elesclomol | Rifabutin | Palmitic acid | Paeoniflorin | Tamoxifen Citrate |
| Related Compound Libraries | Bioactive Compound Library | Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Compound Library | ReFRAME Related Library | HIF-1 Signaling Pathway Compound Library | Anti-Cancer Clinical Compound Library | Drug Repurposing Compound Library | Inhibitor Library | Bioactive Compounds Library Max | Anti-Cancer Drug Library | Anti-Cancer Active Compound Library |



 United States
United States