98849-88-8
 98849-88-8 結(jié)構(gòu)式
98849-88-8 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
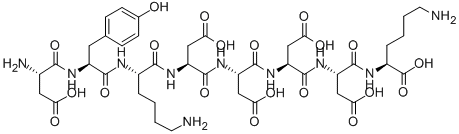
L-LYSINE, L-Α-ASPARTYL-L-TYROSYL-L-LYSYL-L-Α-ASPARTYL-L-Α-ASPARTYL-L-Α-ASPARTYL-L-Α-ASPARTYL-
FLAG tag Peptide
FLAG PEPTIDE, >98%
FLAG Tag Peptide,F(xiàn)LAG epitope
FLAG PEPTIDE|DYKDDDDK|ASP-TYR-LYS-ASP-ASP-ASP-ASP-LYS
FLAG peptide,DYKDDDDK,Asp-Tyr-Lys-Asp-Asp-Asp-Asp-Lys, >98%
(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-6-amino-2-[[(2S)-2-[[(2S)-2-amino-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-(4-hydroxyphenyl)propanoyl]amino]hexanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]-3-carboxypropanoyl]amino]hexanoic acid
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2025/05/22 | HY-P0223 | FLAG肽 FLAG peptide | 98849-88-8 | 1 mg | 500元 |
| 2025/05/22 | HY-P0223 | FLAG肽 FLAG peptide | 98849-88-8 | 5 mg | 900元 |
| 2025/05/22 | HY-P0223 | FLAG肽 FLAG peptide | 98849-88-8 | 10 mg | 1300元 |
常見問題列表
Fusion protein technology has become an important tool for solving numerous problems linked to recombinant protein production. The properties of the additional tag facilitate identification and provide a one-step purification procedure of the fusion protein by passing cell extracts or supernatants through columns of an appropriate matrix. FLAG peptide allows elution under non-denaturing conditions. Several antibodies against FLAG peptide have been developed. One antibody, M1, binds the peptide in the presence of bivalent metal cations, preferably Ca 2+ . Elution is effected by chelating agents. Another strategy is competitive elution with excess of free FLAGe peptide. Antibodies M2 and M5 are applied in this procedure. The Flag-tag is first described as a calcium-dependent epitope of a monoclonal antibody. It is a highly acidic octapeptide which can be N-terminally fused to the protein of interest. As a very hydrophilic peptide the Flag–tag has a high surface probability. Flag-fusion proteins can be captured by an immunoaffinity column in the presence of Ca 2+ and eluted byEDTA at low concentrations, neutral pH and thus, nearly physiological conditions.