94535-50-9
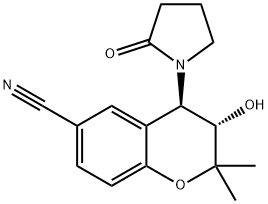 94535-50-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
94535-50-9 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
左色滿卡林
lemakalim
Brn 3622889
levcromakelim
LEVCROMAKALIM
LevkroMakaliM
(3s-trans)-yrrolidinyl)
Potassium Channel,KcsA,Inhibitor,inhibit,BRL38227,BRL-38227,Levcromakalim
(3β,4α)-3-Hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)chroman-6-carbonitrile
(3S,4R)-3-hydroxy-2,2-dimethyl-4-(2-oxopyrrolidin-1-yl)chroman-6-carbonitrile
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2024/11/08 | HY-14255 | 左色滿卡林 Levcromakalim | 94535-50-9 | 2 mg | 800元 |
| 2024/11/08 | HY-14255 | 左色滿卡林 Levcromakalim | 94535-50-9 | 5mg | 1200元 |
| 2024/11/08 | HY-14255 | 左色滿卡林 Levcromakalim | 94535-50-9 | 10 mM * 1 mLin DMSO | 1260元 |
常見問題列表
K + channel
Levcromakalim ((-)-Cromakalim) inhibits spontaneous contractions completely in a glibenclamide-sensitive manner. LevCromakalim (5 μM) inhibits spontaneous contractions, which are recovered by glibenclamide. Levcromakalim (1, 5 and 10 μM) inhibits phasic contractions to 34±21.1%, 20.1±20.0% and 0% of the control (n=5, respectively; P<0.05). Glibenclamide reverses the inhibition of spontaneous isometric contractions caused by LevCromakalim (5 μM) to 84±1.5% of the control (n=5; P<0.05). Levcromakalim (20 and 100 μM) also inhibits oxytocin (OXT) (10 nM)-induced phasic contractions to 34±21.4% and 14±12.6% of the control (n=6 and 4, respectively; P<0.05). Glibenclamide reverses the inhibition of spontaneous isometric contractions by LevCromakalim (100 μM) to 79±3.5% of the control (n=4; P<0.05). Tonic contraction by OXT is also suppressed by Cromakalim in a glibenclamide-sensitive manner.The function of the K ATP channels is examined with the specific channel opener LevCromakalim (Cromakalim). LevCromakalim induces dose-dependent relaxation in both the young and old mesenteric artery (MAs); and there is no difference in relaxation with age. However, the relaxation is markedly reduced in response to the high-salt (HS) diet in the old MAs (P<0.05). Maximum dilations to Levcromakalim (10 -4 M) are 97 ± 3% in the young MAs versus 98 ± 1% in the young salt arteries, while dilations are 99±0.7% in the old MAs when compared with 85 ± 5% in the old salt arteries (P<0.05).