861998-00-7
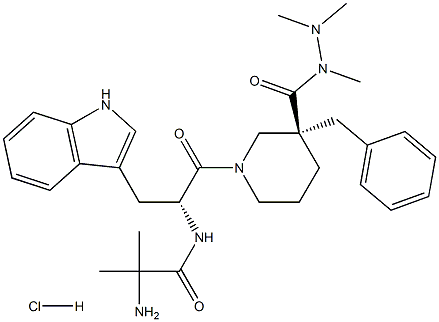 861998-00-7 結(jié)構(gòu)式
861998-00-7 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
阿拉莫林鹽酸鹽
饑餓素受體(GHRELIN RECEPTOR)激動(dòng)劑(ANAMORELIN HYDROCHLORIDE)
AnaMorelin HCl
RC 1291 hydrochloride
ONO-7643 hydrochloride
AnaMorelin hydrochloride
Anamorelin (RC-1291) HCl
Anamorelin (RC-1291) hydrochloride
Anamorelin hydrochloride (RC-1291 hydrochloride
(3R)-1-(2-Methylalanyl-D-tryptophyl)-3-(phenylmethyl)-3-piperidinecarboxylic acid trimethylhydrazide monohydrochloride
RC-1291 HYDROCHLORIDE
ONO-7643 HYDROCHLORIDE
RC1291 HYDROCHLORIDE
ONO7643 HYDROCHLORIDE
RC 1291 HYDROCHLORIDE
ONO 7643 HYDROCHLORIDE
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
| 報(bào)價(jià)日期 | 產(chǎn)品編號(hào) | 產(chǎn)品名稱 | CAS號(hào) | 包裝 | 價(jià)格 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-14734A | 阿拉莫林鹽酸鹽 Anamorelin hydrochloride | 861998-00-7 | 1 mg | 320元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-14734A | 阿拉莫林鹽酸鹽 Anamorelin hydrochloride | 861998-00-7 | 5mg | 1000元 |
| 2025/02/08 | HY-14734A | 阿拉莫林鹽酸鹽 Anamorelin hydrochloride | 861998-00-7 | 10mM * 1mLin DMSO | 1283元 |
常見問題列表
Ki: 0.7 nM (ghrelin receptor)
EC50: 0.74 nM (ghrelin receptor)
In the FLIPR assay, Anamorelin (ANAM) shows significant agonist activity on the ghrelin receptor, with EC 50 value of 0.74 nM. No significant antagonist activity is observed with Anamorelin at concentrations of up to 1,000 nM. In the binding experiments, Anamorelin binds to the ghrelin receptor with a binding affinity constant (K i ) of 0.70 nM. In the competition assay with radiolabeled ibutamoren ( 35 S-MK-677; another ghrelin receptor agonist) Anamorelin (ANAM) is also found to bind with high affinity to the ghrelin receptor (IC 50 =0.69 nM). In rat pituitary cells incubated with Anamorelin, there is a dose-dependent stimulatory effect on GH release and the potency (EC 50 ) is 1.5 nM. Anamorelin is screened for activity against a set of over 100 receptors, ion channels, transporters, and enzymes. Anamorelin demonstrates binding to the tachykinin neurokinin 2 (NK 2 ) site (IC 50 =0.021 μM); however, a subsequent NK 2 functional assay demonstrates no functional activity.
In rats, Anamorelin (ANAM) at an oral dose of 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg once daily significantly increases both food intake and body weight from Day 2 to Day 7 of treatment compared with the vehicle control. The cumulative change in food intake and weight gain increases dose-dependently, and these changes are significant at all dose levels (P<0.05) compared to the control. Administration of Anamorelin at a single oral dose of 3, 10, or 30 mg/kg induces a dose-dependent increase in plasma GH levels and GH AUC 0-6h in rats.