861393-28-4
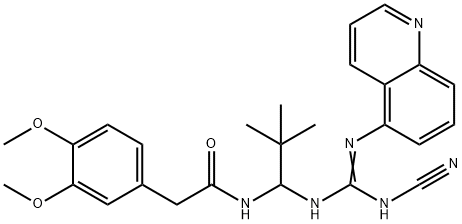 861393-28-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
861393-28-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
N-[1-[[(氰基氨基)(5-喹啉亞氨基)甲基]氨基]-2,2-二甲基丙基]-3,4-二甲氧基苯乙酰胺
A-740003
A-740003, >=99%
A 740003
A740003
A740003 - CAS 861393-28-4 - Calbiochem
P2XRs,P2X Receptor,inhibit,A-740003,A740003,Inhibitor
(E)-N-(1-((Cyanamido(quinolin-5-ylamino)methylene)amino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyp
N-(1-(3-Cyano-2-(quinolin-5-yl)guanidino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl)-2-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)acetamide
N-[1-[[(Cyanoamino)(5-quinolinylimino)methyl]amino]-2,2-dimethylpropyl]-3,4-dimethoxybenzeneacetamide
N-[1-[[(Cyanoamino)(5-quinolinylamino)methylene]amino]-2,2-dimethylpropyl]-3,4-dimethoxybenzeneacetamide
物理化學(xué)性質(zhì)
常見問題列表
| Target | Value |
|
rat P2X7 receptor
(Cell-free assay) | 18 nM |
|
human P2X7 receptor
(Cell-free assay) | 40 nM |
|
IL-1β pore formation
(Cell-based assay) | 92 nM |
|
IL-1β release
(Cell-based assay) | 156 nM |
A 438079 or A 740003 (10 μM) significantly blocks the sustained phase of the BzATP-induced response. A-740003 infusion reduces SE-induced TNF-α expression in dentate granule cells. A-740003 infusions increases SE-induced neuronal death. A-740003 and A-438079 show significantly greater potency in blocking P2X7 receptor activation across all species compared with other antagonists. A-740003 and A-438079 show greater activity at rat and human, as compared with mouse P2X7 receptors. A-740003 potently blocks agonist-evoked IL-1β release with (IC 50 =156 nM) and pore formation (IC 50 =92 nM) in differentiated human THP-1 cells.
Systemic administration of A-740003 produces dose-dependent antinociception in a spinal nerve ligation model (ED 50 =19 mg/kg i.p.) in the rat. A-740003 also attenuates tactile allodynia in two other models of neuropathic pain, chronic constriction injury of the sciatic nerve and vincristine-induced neuropathy. In addition, A-740003 effectively reduces thermal hyperalgesia observed following intraplantar administration of carrageenan or complete Freund's adjuvant (ED 50 =38-54 mg/kg i.p.). A-740003 is ineffective in attenuating acute thermal nociception in normal rats and does not alter motor performance at analgesic doses.
