20153-98-4
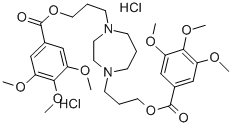 20153-98-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
20153-98-4 結(jié)構(gòu)式
基本信息
1,4-雙[3-(3,4,5-三甲氧基苯甲酰氧基)丙基]高哌嗪二鹽酸鹽
k-285
C12954
C-4898
labitan
comelian
cormelian
astac4898
DILAZEP DIHYDROCHLORIDE
h)dipropanol,dihydrochloride
物理化學性質(zhì)
安全數(shù)據(jù)
常見問題列表
Adenosine uptake
The uptake mechanism has been studied extensively in vitro and Dilazep, NBI and Dipyridamole have been reported to inhibit the uptake of adenosine into different cells. Of these compounds, Dilazep and NBI are almost 10 times more potent than Dipyridamole. In addition, only Dilazep is water soluble and no solubility aiding organic solvent is needed for preparing an aqueous solution.
After administration of Dilazep, even low doses (0.04-0.1 mg/kg/min) of exogenous adenosine significantly increases superior mesenteric arterial conductance (SMAC) and elevates arterial plasma adenosine concentration. The increased adenosine levels were highly correlated with the increased percentage of change of SMAC and values for R
max
and EC
50
were 193.4% change of SMAC and 2.8 μM, respectively. Administration of bolus doses of 8-phenyltheophylline abolishes the ability of Dilazep to potentiate vasodilation, but did not affect isoproterenol-induced relaxation.
Dilazep inhibits the phospholipase activation in reperfused heart mitochondria and also inhibits the lipid peroxidation caused by cerebral ischemia and reperfusion. Dilazep may prevent ischemic cerebral injury due to an increase in cerebral blood flow and/or its protective effects on vascular endothelial cell membrane.
