| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Ramiprilat | [CAS]
87269-97-4 | [Synonyms]
RAMIPRILAT
Ramiprilate
HOE 498 Diacid
Ramipril Diacid
RAMIPRILAT HYDRATE
RaMipril EP IMpurity E
RaMipril IMpurity-E (EP)
Ramiprilat, ammonium salt
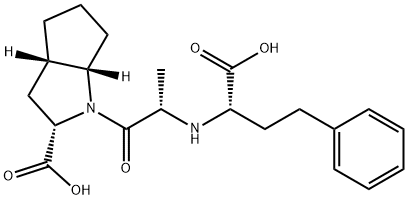
(2S,3aS,6aS)-1-[(S)-N-[(S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]alanyl]octahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
(2S,3aS,6aS)-1-((S)-N-((S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)alanyl)tetrahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
(2S,3aβ,6aβ)-1-[(S)-2-[[(S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]propionyl]octahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2α-carboxylic acid
ramiprilat:(2s,3as,6as)-1-((s)-n-((s)-1-carboxy-3-phenylpropyl)alanyl)tetrahydrocyclopenta(b)pyrrole-2-carboxylic acid
(2S,3aS,6aS)-1-[(2S)-2-[[(1S)-1-Carboxy-3-phenylpropyl]amino]-1-oxopropyl]octahydrocyclopenta[b]pyrrole-2-carboxylic Acid | [EINECS(EC#)]
258-696-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C21H28N2O5 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00865787 | [MOL File]
87269-97-4.mol | [Molecular Weight]
388.46 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Appearance]
White to Off-White Solid | [Melting point ]
139-141°C | [Boiling point ]
632.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.273±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Refrigerator, Under Inert Atmosphere | [solubility ]
DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
2.20±0.10(Predicted) | [color ]
White to Pale Yellow | [Stability:]
Hygroscopic |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White to Off-White Solid | [Uses]
A metabolite of Ramipril (R111000). | [Definition]
ChEBI: A dipeptide that is the active metabolite of ramipril. An angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, used to treat high blood pressure and congestive heart failure. | [Description]
Ramiprilat is the active metabolite of ramipril (Item No. 15558) and functions as an angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor (pKi = 9.08 in human heart) to suppress the conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II and the degradation of bradykinin, thereby preventing vasoconstriction.1,2 Furthermore, ramiprilat is reported to interfere with the targeting of B2 kinin receptors to endothelial cell membranes further preventing bradykinin signaling.2 In addition to its cardioprotective effects in both animal models and clinical studies, ramiprilat has been reported to inhibit matrix metalloproteinase-3 and -9 activity in isolated Crohn’s disease fistulas.3,4 | [in vitro]
pretreatment with ramiprilat could significantly attenuate the recovery of b2 kinin receptors in while increasing that from membranes lacking caveolin, and such effect was not because of the inhibition of bradykinin degradation. ramiprilat could also decrease [3h]bradykinin binding to cr membranes. in addition, ramiprilat treatment led to reactivation of the b2 receptor in bradykinin-stimulated cells [1]. | [in vivo]
in previous animal study, when compared with the control rats, diabetic rats showed decreased creatinine clearance rate, increased urinary protein excretion and blood pressure, as well as development of tubulointerstitial fibrosis, glomerulosclerosis, and inflammatory cell infiltration. furthermore, the blocking angiotensin ii with ramipril (the prodrug of ramiprilat) was able to significantly improve all of these parameters [2]. | [References]
[1] t. benzing, i. fleming, a. blaukat, et al. angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor ramiprilat interferes with the sequestration of the b2 kinin receptor within the plasma membrane of native endothelial cells. circulation 99(15), 2034-2040 (1999).
[2] li c, yang cw, park cw, ahn hj, kim wy, yoon kh, suh sh, lim sw, cha jh, kim ys, kim j, chang ys, bang bk. long-term treatment with ramipril attenuates renal osteopontin expression in diabetic rats. kidney int. 2003 feb;63(2):454-63.
[3] warner gt, perry cm. ramipril: a review of its use in the prevention of cardiovascular outcomes. drugs. 2002;62(9):1381-405. |
|
|