| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
Carboxymethyl chitosan | [CAS]
83512-85-0 | [Synonyms]
CARBOXYMETHYL CHITOSAN
N-Carboxymethylchitosan
CarboxylMethyl Chitosan
Chitosan, N-(carboxymethyl) | [EINECS(EC#)]
1308068-626-2 | [Molecular Formula]
C20H37N3O14 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00677440 | [MOL File]
83512-85-0.mol | [Molecular Weight]
543.519 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
600 °C | [storage temp. ]
Room Temperature, under inert atmosphere | [solubility ]
Aqueous Acid (Slightly, Heated, Sonicated), Water (Sonicated) | [form ]
Solid | [color ]
Off-White to Pale Beige |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
Forms gel with water, lower degree of substitution than 5-00936 | [Uses]
Carboxymethyl Chitosan is a useful polymeric modifier, used as an absorbent for removal of mercury ions, and as binding agent for silver nanoparticle coated cotton fabric. |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Application]
Carboxymethyl chitosan is a biocompatible and biodegradable material that is suitable for various applications such as sustained or controlled release drug delivery, pH-responsive drug delivery, gene delivery as permeation enhancer, Carboxymethyl chitosan is a coating material on nanocarriers.
| [Chitosan VS Carboxymethyl Chitosan]
Compared to chitosan, Carboxymethyl chitosan not only can be applied in wider pH ranges of water since its higher stability, but also has a higher hydrophilicity . The larger specific surface area, a multitude of functional groups and higher hydrophilicity of Carboxymethyl chitosan are expected to play an essential role in more efficiently coordinating with mental oxide and flocculate solrelieving tickle. Carboxymethyl chitosan is an amphoteric poly-saccharide that possesses pH-sensitive property, since it bears both acidic (-COOH) and basic groups (-NH2).
| [Preparation]
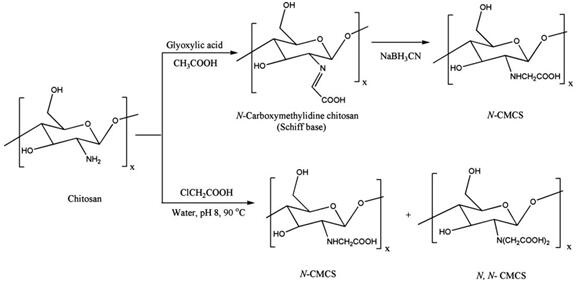
Carboxymethyl chitosan can be obtained by direct alkylation of chitosan. The Carboxymethyl chitosan achieved can be in many types: N-carboxymethyl chitosan (N-CMCS), O-carboxymethyl chitosan (O-CMCS), N,O-carboxymethyl chitosan (N,O-CMCS) and N,N-carboxymethyl chitosan (N,N-CMCS). Different reaction conditions will result in the N vs. O selectivity and different degree of substitution (DS). Carboxymethyl chitosan possesses high viscosity, large hydrodynamic volume, film- and gel-forming capabilities together with the other useful properties, such as biocompatibility, biodegradation, biological activity and low toxicity, all of which make it an attractive option in connection with its use in foods and cosmetics.
|
|
|