| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
DM4 | [CAS]
796073-69-3 | [Synonyms]
Mertansine Impurity 1
DM4 top3
N2'-Deacetyl-N2'-(4-mercapto-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl)-maytansine
Maytansine, N2'-deacetyl-N2'-(4-mercapto-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl)- | [Molecular Formula]
C38H54ClN3O10S | [MDL Number]
MFCD28144516 | [MOL File]
796073-69-3.mol | [Molecular Weight]
780.37 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
185-187 °C (decomp) | [Boiling point ]
943.2±65.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.29±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C | [solubility ]
DMSO : 100 mg/mL (128.14 mM) | [form ]
Solid | [pka]
9.82±0.70(Predicted) | [color ]
White to light yellow |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Structure]
Structurally, maytansinoid derivatives DM1, DM3, and DM4 differ based on the number of methyl groups present on the carbon adjacent to sulfur—zero, one, or two, respectively. The introduction of methyl groups contributes to the heightened potency of the free drug, likely due to increased hydrophobicity and improved membrane permeability. DM4 is a thiol-containing compound that undergoes methylation within cells through the activity of methyltransferases, forming S-Me-DM4. This metabolite demonstrates notable cytotoxicity. Importantly, both DM4 and S-Me-DM4 can pass through cell membranes, leading to an enhanced phenomenon known as the "bystander effect," where the drug can diffuse out of a targeted cell into adjacent cells[1].
|
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Ravtansine (DM4) is a maytansinoid, a chemical derivative of maytansine being investigated as the cytotoxic payload of a number of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs).M4 is is an antitubulin agent that inhibit cell division. DM4 can be used in the preparation of antibody drug conjugate. | [Uses]
N2''-Deacetyl-N2''-(4-mercapto-4-methyl-1-oxopentyl)-maytansine is an intermediate used to prepare semisynthetic maytansine analogs which can be conjugated with antibodies for the targeted treatment of cancer. | [Biological Activity]
The anticancer properties of maytansinoids have been attributed to their ability to disrupt microtubule function. The maytansinoid emtansine (DM1), for example, binds at the ends of microtubules and thereby suppress their dynamic instability. Other maytansinoids include: Ansamitocin; Mertansine/emtansine (DM1); Ravtansine/soravtansine (DM4). | [Synthesis]
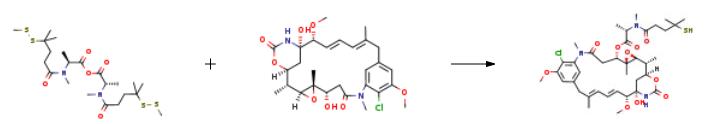
A solution of N-methyl-N-(4-methyldithio-4-methyl-1-oxopropyl)-L-alanine (36.6 mg, 0.313 mmol) and 1,3-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide (13.51 mg, 0.065 mmol) was prepared in CH2Cl2 (0.5 mL) in a round bottom flask equipped with a stir bar and maintained under an argon atmosphere. The solution stirred vigorously at room temperature for 30 minutes as the symmetrical anhydride formed. The reaction mixture was filtered through glass wool and added to a reaction flask containing maytansinol (12.3 mg, 0.022 mmol) and zinc bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)amide] (42.5 mg, 0.109 mmol) prepared in CH2Cl2 (1 mL). The reaction proceeded at room temperature under an argon atmosphere with stirring. After 3 hours, an additional 5 equivalents of zinc bis[bis(trimethylsilyl)amide] (42.5 mg, 0.109 mmol) were added to the reaction vessel and the reaction proceeded overnight. Analytical thin layer chromatography (Analtech Uniplate, 2.5?á10 cm, 250 micron), eluting in a mixture of methylene chloride and methanol (95:5, v/v) indicated the formation of the desired N-methyl-L-alanyl ester of maytansinol at C3. The degree of conversion of the reaction was determined by analytical HPLC analysis using a Vydac protein & peptide C18 column (4.6?á250 mm) at a flow rate of 1.50 mL/min, eluting with a gradient of water and acetonitrile, as follows: Time (min) % A (water) % B (acetonitrile) 0 95 5 2.5 95 5 32 5 95 35 5 95 Under these conditions the thiol containing product eluted at 20.75 min with no detected D-isomer. MS: m/z found 780.8 (M+Na+) calculated 781.4. | [in vitro]
DM4, a structural analogue of maytansine, is a new thiol-containing and potent maytansinoid. DM4 is a cytotoxic maytansinoid drug. It is synthesized in order to link maytansinoids to antibodies via disulfide bonds. Maytansinoids inhibit tubulin polymerization and microtubule assembly and enhance microtubule destabilization, so there is potent suppression of microtubule dynamics resulting in a mitotic block and subsequent apoptotic cell death. | [storage]
Store at -20°C | [References]
[1] Giulio Lovato . “HPLC-DAD validated method for DM4 and its metabolite S-Me-DM4 quantification in biological matrix for clinical and pharmaceutical applications.” Journal of pharmaceutical and biomedical analysis 235 (2023): Article 115642.
|
|
|