| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
8-Gingerol | [CAS]
30462-35-2 | [Synonyms]
TFDG
theaflavin 3
8-Gingerol Hplc
8-GINGEROL, HPLC 98%
Theaflavin 3,3&rsquo
THEAFLAVIN 3,3'-DIGALLATE
THEAFLAVIN 3,3'-DI-O-GALLATE
Theaflavin-3,3-digallate(TF3)
Theaflavin 3,3'-digallate USP/EP/BP
3,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,8-bis[[(2R)-3,4-dihydro-3α-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyloxy)-5,7-dihydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran]-2α-yl]-5H-benzocycloheptene-5-one
3,4,6-Trihydroxy-1,8-bis[[(2R)-3,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-3α-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyloxy)-2H-1-benzopyran]-2α-yl]-5H-benzocycloheptene-5-one
3,4,5-Trihydroxybenzoic acid (3,4,6-trihydroxy-5-oxo-5H-benzocycloheptene-1,8-diyl)bis[(2R,3R)-3,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2,3-diyl] ester
Benzoic acid, 3,4,5-trihydroxy-, 1,1'-[(3,4,6-trihydroxy-5-oxo-5H-benzocycloheptene-1,8-diyl)bis[(2R,3R)-3,4-dihydro-5,7-dihydroxy-2H-1-benzopyran-2,3-diyl]] ester
[(2R,3R)-3-[1-[5,7-dihydroxy-2-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-chroman-3-yl]-3,4,6-trihydroxy-5-oxo-benzo[7]annulen-8-yl]-5,7-dihydroxy-chroman-2-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
[(2R,3R)-2-[1-[(2R,3R)-5,7-dihydroxy-3-(3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoyl)oxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-2-yl]-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-oxobenzo[7]annulen-8-yl]-5,7-dihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-3-yl] 3,4,5-trihydroxybenzoate
TheaflAVin-3-3’-digallateQ: What is
TheaflAVin-3-3’-digallate Q: What is the CAS Number of
TheaflAVin-3-3’-digallate Q: What is the storage condition of
TheaflAVin-3-3’-digallate Q: What are the applications of
TheaflAVin-3-3’-digallate | [Molecular Formula]
C43H32O20 | [MDL Number]
MFCD06797365 | [MOL File]
30462-35-2.mol | [Molecular Weight]
868.7 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
226~230℃ | [Boiling point ]
1352.6±65.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.97±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) | [storage temp. ]
Store at -20°C, sealed storage, away from moisture and light | [solubility ]
DMSO : 41.67 mg/mL (47.97 mM; Need ultrasonic) | [form ]
neat | [pka]
6.55±0.20(Predicted) | [color ]
Red-purple | [InChIKey]
ZEASWHWETFMWCV-ISBUVJFSSA-N | [CAS DataBase Reference]
30462-35-2 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Description]
Theaflavin-3,3''-digallate (TFDG) is a major polyphenol found in black tea with diverse biological activities.1,2,3 It has antioxidant activity, inhibiting the formation of superoxide radicals, singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals in vitro (IC50s = 26.7, 0.83, 0.39, and 25.07 μmol/L, respectively).1 It also reduces hydroxyl radical-induced damage to plasmid DNA. TFDG (12.5-50 μM) prevents LPS-induced release of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, expression of JNK and p38, and nuclear translocation of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 cells.2 In vivo, TFDG reduces serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 and decreases pulmonary edema, pulmonary congestion, and thickening of the alveolar wall in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury. It also inhibits osteoclast formation, polarization, and osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro and reduces titanium particle-induced bone erosion and the number of mature osteoclasts in mice in a dose-dependent manner.3 | [Uses]
Theaflavin 3,3''-Digallate has been found to be an inhibitor against human pancreatic α-Amylase. | [Definition]
ChEBI:Theaflavin 3,3'-digallate is a catechin. | [General Description]
Theaflavin 3,3′-digallate is a theaflavin derivative, exhibiting antioxidative, anti-inflammatory, and anti-tumor activities. It is also associated with many beneficial health effects, including the prevention of cancer and heart disease. | [Synthesis]
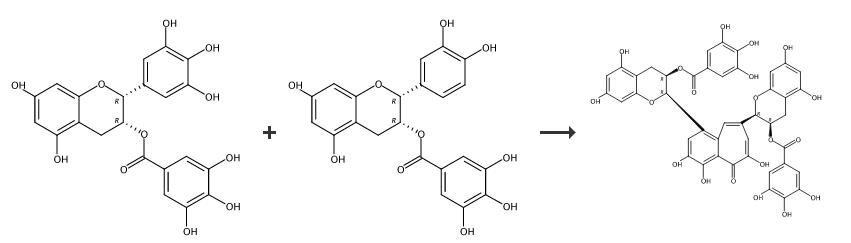
1. Enzymatic Oxidation and Isolation of Theaflavins, EC (1 g, 3.5 mmol) and EGC (1 g, 3.3 mmol) were dissolved into the 200 mL of phosphate-citrate buffer (50 mM, pH 5.0) along with 2 g of crude PPO enzyme. The enzymatic oxidation was carried out at room temperature for 6 hour with stirring. The reaction solution was then subjected to fractionation with the same volume of ethyl acetate with three times. Then, the organic layer was concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residues were subjected to Sephadex LH-20 column chromatography eluting with gradient of ethanol to 20% of acetone in ethanol. Among the collected 14 fractions (each c.a. 90 mL), 8-10 fractions were combined, and concentrated under reduced pressure. The resulting residue was subjected to further purification on a RP-18 silica gel column eluting with gradient of 40%~50% of aqueous methanol. During elution, 38 fractions (each c.a. 13 mL) were received. Among them, 10-17 fractions were combined, and concentrated under reduced pressure, and were subjected to freeze-drying. It yielded deep-reddish color of compound 1 (280 mg). Along with the same enzyme reaction and isolation procedure, compound 2 was obtained from EC and EGCG reaction. The enzymatic oxidation of EGC and ECG, ECG and EGCG reaction yielded compound 3 and compound 4, respectively. compound 4, Theaflavin 3,3'-digallate 1H NMR (CD3OD, 600 MHz): |?H 7.79 1H s, 7.76 1H s, 7.47 1H s, 6.88 2H s, 6.80 2H s, 6.07 1H d, J=2.4 Hz, 6.03 2H d, J=2.4 Hz, 6.00 1H d, J=2.4 Hz, 5.86 1H brs, 5.76 1H m, 5.67 1H m, 5.21 1H s, 3.17 1H dd, J=4.8, 16.8 Hz, 3.09 1H dd, J=4.8, 17.4, 2.91 2H m. | [storage]
Store at -20°C, sealed storage, away from moisture and light |
| Questions And Answer | Back Directory | [Biological Activities]
Theaflavin-3,3'-digallate (TFDG) is a major polyphenol found in black tea with diverse biological activities. It has antioxidant activity, inhibiting the formation of superoxide radicals, singlet oxygen, hydrogen peroxide, and hydroxyl radicals in vitro (IC50s = 26.7, 0.83, 0.39, and 25.07 µmol/L, respectively).
It also reduces hydroxyl radical-induced damage to plasmid DNA. TFDG (12.5-50 µM) prevents LPS-induced release of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, expression of JNK and p38, and nuclear translocation of NF-κB in RAW 264.7 cells [2]. In vivo, TFDG reduces serum levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 and decreases pulmonary edema, pulmonary congestion, and thickening of the alveolar wall in a mouse model of LPS-induced acute lung injury. It also inhibits osteoclast formation, polarization, and osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro and reduces titanium particle-induced bone erosion and the number of mature osteoclasts in mice in a dose-dependent manner.
|
|
|