| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
HPMDA | [CAS]
2754-41-8 | [Synonyms]
HPMDA
H6-PDA
Colorless Pi
1,2,4,5-cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhyd
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetrcarboxylic Dianhydride
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic Dianhydride >
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic acid dianhydride
1,2,4,5-cyclohexanetetrcarboxylic dianhydride(HPMDA)
HPMDA/1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride
Tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']difuran-1,3,5,7(3aH,7aH)
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetertracarboxylicdianhydride(HPMDA)
hexahydro-1H,3H-benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']difuran-1,3,5,7-tetrone
1,2,4,5-cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride (HPMDA)
1H,3H-Benzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']difuran-1,3,5,7-tetrone, hexahydro-
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic acid dianhydride (HPMDA)
Tetrahydrobenzo[1,2-c:4,5-c']difuran-1,3,5,7(3aH,7aH)-tetraone
1,2,4,5-CYCLOHEXANETETRACARBOXYLIC DIANHYDRIDE (HPMDA)2754-41-8
3a,4,4a,7a,8,8a-hexahydrofuro[3,4-f][2]benzofuran-1,3,5,7-tetrone
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic Dianhydride (purified by sublimation) | [EINECS(EC#)]
691-475-9 | [Molecular Formula]
C10H8O6 | [MDL Number]
MFCD13704912 | [MOL File]
2754-41-8.mol | [Molecular Weight]
224.167 |
| Chemical Properties | Back Directory | [Melting point ]
240°C(lit.) | [Boiling point ]
517.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) | [density ]
1.567 | [storage temp. ]
Inert atmosphere,2-8°C | [solubility ]
soluble in Acetone | [form ]
powder to crystal | [color ]
White to Almost white | [InChI]
InChI=1S/C10H8O6/c11-7-3-1-4-6(10(14)16-8(4)12)2-5(3)9(13)15-7/h3-6H,1-2H2 | [InChIKey]
LJMPOXUWPWEILS-UHFFFAOYSA-N | [SMILES]
O1C(=O)C2CC3C(CC2C1=O)C(=O)OC3=O |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Chemical Properties]
White to Almost white powder to crystal. | [Uses]
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride can be used as organic synthesis intermediates and pharmaceutical intermediates, mainly used in laboratory research and development and chemical and pharmaceutical production processes. | [Application]
HPMDA can be used to synthesize polyesters that have four branches (dianhydride is hydrolysed to four carboxylic acids) for multiple functionalities, such as biodegradability, bioimaging and photoactivity. | [General Description]
1,2,4,5-Cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride (HPMDA) has a cyclohexane centre with two carboxylic anhydrides substituents sitting opposite to each other. HPMDA reacts with amines for polyimides or alternatively with alcohols for polyesters. The non-aromatic cyclohexane centre provides local excited state to the synthesized photochromic polyimides showing large contrast of the photo-switching effect (compared to fully aromatized polyimides). The polyimides derived from 1,2,4,5-cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride exhibit high proton conductivity (0.2 ± 0.01 S/cm at 298 K and 95% related humidity). Like other polyimides, the polyimides have excellent chemical and thermal resistance and are used in optical fibre claddings and substrates for microelectronics. | [Synthesis]
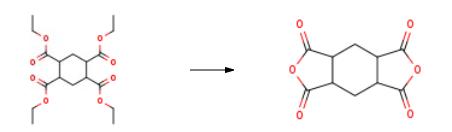
In a 100 mL three-necked flask equipped with a thermometer, a magnetic stirrer, a water separator, and a condenser tube was added 9.64 g of hydrogenatedEthylbenzene tetracarboxylate, 1mL of concentrated sulfuric acid, 5mL of acetic acid and 50mL of xylene were heated to 130??C. During the reaction, the reaction temperature was maintained at reflux, and the reaction continuously removed water for 5 hours. , cooling down to room temperature, suction filtration, filter cake washed with acetone, dried at room temperature under reduced pressure to give white solid 1,2,4,5-cyclohexane tetracarboxylic acid anhydride 4.80g, yield: 82.8%. | [Advantages]
Alicyclic acid anhydrides have been used as raw materials for functional polyimides and functional epoxy resins. Among them, 1,2,4,5-cyclohexanetetracarboxylic dianhydride is used as a raw material for polyimide resins exhibiting particularly good heat resistance, solvent solubility, thermoplasticity, low water absorption, dimensional stability, and like.
|
|
|