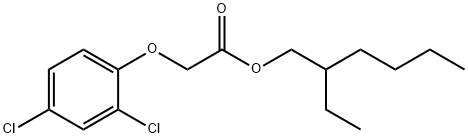
| Identification | Back Directory | [Name]
2,4-D 2-ETHYLHEXYL ESTER | [CAS]
1928-43-4 | [Synonyms]
weed rhop
2-ETHYLHEXYL2,4-D
2,4-d(ethylhexylester)
TIANFU-CHEM 2,4-D 2-ETHYLHEXYL ESTER
2-ethylhexyl(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)ethanoate
2,4-D 2-ethylhexyl ester 100mg [1928-43-4]
2-ethylhexyl 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetate
2,4-D ethylhexyl ester @100 μg/mL in Hexane
2-ethylhexyl 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)ethanoate
(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-aceticaci2-ethylhexylester
2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetic acid 2-ethylhexyl ester
Acetic acid, (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-, 2-ethylhexyl ester
2-Ethylhexyl-2.4-dichlorophenoxy acetate 1g [1928-43-4]
2,4-D 2-ethylhexyl ester Solution in Methanol, 1000μg/mL
Acetic acid, 2-(2,4-dichlorophenoxy)-, 2-ethylhexyl ester | [EINECS(EC#)]
217-673-3 | [Molecular Formula]
C16H22Cl2O3 | [MDL Number]
MFCD00126851 | [MOL File]
1928-43-4.mol | [Molecular Weight]
333.25 |
| Hazard Information | Back Directory | [Uses]
2-Ethylhexyl (2,4-dichlorophenoxy)acetate is used in herbicidal compositions. | [General Description]
Sweet smelling liquid. | [Reactivity Profile]
Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. |
|
|